| Safe Haskell | None |
|---|---|
| Language | Haskell2010 |
Graphics.Rasterific
Contents
Description
Main module of Rasterific, an Haskell rasterization engine.
Creating an image is rather simple, here is a simple example of a drawing and saving it in a PNG file:
import Codec.Picture( PixelRGBA8( .. ), writePng )
import Graphics.Rasterific
import Graphics.Rasterific.Texture
main :: IO ()
main = do
let white = PixelRGBA8 255 255 255 255
drawColor = PixelRGBA8 0 0x86 0xc1 255
recColor = PixelRGBA8 0xFF 0x53 0x73 255
img = renderDrawing 400 200 white $
withTexture (uniformTexture drawColor) $ do
fill $ circle (V2 0 0) 30
stroke 4 JoinRound (CapRound, CapRound) $
circle (V2 400 200) 40
withTexture (uniformTexture recColor) .
fill $ rectangle (V2 100 100) 200 100
writePng "yourimage.png" img

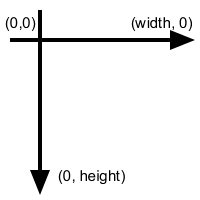
The coordinate system is the picture classic one, with the origin in the upper left corner; with the y axis growing to the bottom and the x axis growing to the right:
- fill :: [Primitive] -> Drawing px ()
- fillWithMethod :: FillMethod -> [Primitive] -> Drawing px ()
- withTexture :: Texture px -> Drawing px () -> Drawing px ()
- withClipping :: (forall innerPixel. Drawing innerPixel ()) -> Drawing px () -> Drawing px ()
- withTransformation :: Transformation -> Drawing px () -> Drawing px ()
- stroke :: Float -> Join -> (Cap, Cap) -> [Primitive] -> Drawing px ()
- dashedStroke :: DashPattern -> Float -> Join -> (Cap, Cap) -> [Primitive] -> Drawing px ()
- dashedStrokeWithOffset :: Float -> DashPattern -> Float -> Join -> (Cap, Cap) -> [Primitive] -> Drawing px ()
- printTextAt :: Font -> Int -> Point -> String -> Drawing px ()
- renderDrawing :: forall px. (Pixel px, Pixel (PixelBaseComponent px), Modulable (PixelBaseComponent px), PixelBaseComponent (PixelBaseComponent px) ~ PixelBaseComponent px) => Int -> Int -> px -> Drawing px () -> Image px
- pathToPrimitives :: Path -> [Primitive]
- type Texture px = SamplerRepeat -> Float -> Float -> px
- type Drawing px = Free (DrawCommand px)
- class (Ord a, Num a) => Modulable a
- data V2 a :: * -> * = V2 !a !a
- type Point = V2 Float
- type Vector = V2 Float
- data CubicBezier = CubicBezier {
- _cBezierX0 :: !Point
- _cBezierX1 :: !Point
- _cBezierX2 :: !Point
- _cBezierX3 :: !Point
- data Line = Line {}
- data Bezier = Bezier {}
- data Primitive
- data Path = Path {}
- data PathCommand
- class Transformable a where
- class PointFoldable a where
- foldPoints :: (b -> Point -> b) -> b -> a -> b
- line :: Point -> Point -> [Primitive]
- rectangle :: Point -> Float -> Float -> [Primitive]
- roundedRectangle :: Point -> Float -> Float -> Float -> Float -> [Primitive]
- circle :: Point -> Float -> [Primitive]
- ellipse :: Point -> Float -> Float -> [Primitive]
- polyline :: [Point] -> [Primitive]
- polygon :: [Point] -> [Primitive]
- drawImageAtSize :: (Pixel px, Modulable (PixelBaseComponent px)) => Image px -> StrokeWidth -> Point -> Float -> Float -> Drawing px ()
- drawImage :: (Pixel px, Modulable (PixelBaseComponent px)) => Image px -> StrokeWidth -> Point -> Drawing px ()
- clip :: Point -> Point -> Primitive -> [Primitive]
- bezierFromPath :: [Point] -> [Bezier]
- lineFromPath :: [Point] -> [Line]
- cubicBezierFromPath :: [Point] -> [CubicBezier]
- data Join
- data Cap
- data SamplerRepeat
- data FillMethod
- type DashPattern = [Float]
- dumpDrawing :: Show px => Drawing px () -> String
Rasterization command
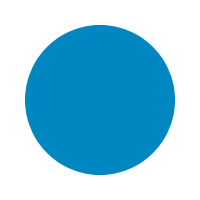
fill :: [Primitive] -> Drawing px () Source
Fill some geometry. The geometry should be "looping", ie. the last point of the last primitive should be equal to the first point of the first primitive.
The primitive should be connected.
fill $ circle (V2 100 100) 75
fillWithMethod :: FillMethod -> [Primitive] -> Drawing px () Source
This function let you choose how to fill the primitives
in case of self intersection. See FillMethod documentation
for more information.
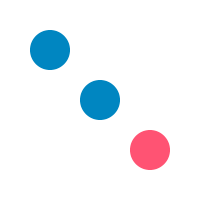
withTexture :: Texture px -> Drawing px () -> Drawing px () Source
Define the texture applyied to all the children draw call.
withTexture (uniformTexture $ PixelRGBA8 0 0x86 0xc1 255) $ do
fill $ circle (V2 50 50) 20
fill $ circle (V2 100 100) 20
withTexture (uniformTexture $ PixelRGBA8 0xFF 0x53 0x73 255)
$ circle (V2 150 150) 20
Arguments
| :: (forall innerPixel. Drawing innerPixel ()) | The clipping path |
| -> Drawing px () | The actual geometry to clip |
| -> Drawing px () |
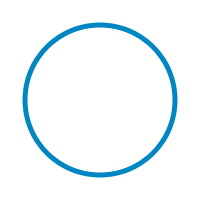
Draw some geometry using a clipping path.
withClipping (fill $ circle (V2 100 100) 75) $
mapM_ (stroke 7 JoinRound (CapRound, CapRound))
[line (V2 0 yf) (V2 200 (yf + 10))
| y <- [5 :: Int, 17 .. 200]
, let yf = fromIntegral y ]

withTransformation :: Transformation -> Drawing px () -> Drawing px () Source
Draw all the sub drawing commands using a transformation.
Arguments
| :: Float | Stroke width |
| -> Join | Which kind of join will be used |
| -> (Cap, Cap) | Start and end capping. |
| -> [Primitive] | List of elements to render |
| -> Drawing px () |
Will stroke geometry with a given stroke width. The elements should be connected
stroke 5 JoinRound (CapRound, CapRound) $ circle (V2 100 100) 75
Arguments
| :: DashPattern | Dashing pattern to use for stroking |
| -> Float | Stroke width |
| -> Join | Which kind of join will be used |
| -> (Cap, Cap) | Start and end capping. |
| -> [Primitive] | List of elements to render |
| -> Drawing px () |
With stroke geometry with a given stroke width, using a dash pattern.
dashedStroke [5, 10, 5] 3 JoinRound (CapRound, CapStraight 0)
[line (V2 0 100) (V2 200 100)]

Arguments
| :: Float | Starting offset |
| -> DashPattern | Dashing pattern to use for stroking |
| -> Float | Stroke width |
| -> Join | Which kind of join will be used |
| -> (Cap, Cap) | Start and end capping. |
| -> [Primitive] | List of elements to render |
| -> Drawing px () |
With stroke geometry with a given stroke width, using a dash pattern. The offset is there to specify the starting point into the pattern, the value can be negative.
dashedStrokeWithOffset 3 [5, 10, 5] 3 JoinRound (CapRound, CapStraight 0)
[line (V2 0 100) (V2 200 100)]

Arguments
| :: Font | Drawing font |
| -> Int | font Point size |
| -> Point | Baseline begining position |
| -> String | String to print |
| -> Drawing px () |
Draw a string at a given position. Text printing imply loading a font, there is no default font (yet). Below an example of font rendering using a font installed on Microsoft Windows.
import Graphics.Text.TrueType( loadFontFile )
import Codec.Picture( PixelRGBA8( .. ), writePng )
import Graphics.Rasterific
import Graphics.Rasterific.Texture
main :: IO ()
main = do
fontErr <- loadFontFile "C:/Windows/Fonts/arial.ttf"
case fontErr of
Left err -> putStrLn err
Right font ->
writePng "text_example.png" .
renderDrawing 300 70 (PixelRGBA8 255 255 255 255)
. withTexture (uniformTexture $ PixelRGBA8 0 0 0 255) $
printTextAt font 12 (V2 20 40) "A simple text test!"

You can use any texture, like a gradient while rendering text.
Arguments
| :: (Pixel px, Pixel (PixelBaseComponent px), Modulable (PixelBaseComponent px), PixelBaseComponent (PixelBaseComponent px) ~ PixelBaseComponent px) | |
| => Int | Rendering width |
| -> Int | Rendering height |
| -> px | Background color |
| -> Drawing px () | Rendering action |
| -> Image px |
Function to call in order to start the image creation. Tested pixels type are PixelRGBA8 and Pixel8, pixel types in other colorspace will probably produce weird results.
pathToPrimitives :: Path -> [Primitive] Source
Transform a path description into a list of renderable primitives.
Rasterization types
type Texture px = SamplerRepeat -> Float -> Float -> px Source
A texture is just a function which given pixel coordinate give back a pixel. The float coordinate type allow for transformations to happen in the pixel space.
class (Ord a, Num a) => Modulable a Source
Typeclass intented at pixel value modulation. May be throwed out soon.
Minimal complete definition
emptyValue, fullValue, clampCoverage, modulate, modiv, alphaOver, alphaCompose
Geometry description
data V2 a :: * -> *
A 2-dimensional vector
>>>pure 1 :: V2 IntV2 1 1
>>>V2 1 2 + V2 3 4V2 4 6
>>>V2 1 2 * V2 3 4V2 3 8
>>>sum (V2 1 2)3
Constructors
| V2 !a !a |
Instances
data CubicBezier Source
Describe a cubic bezier spline, described using 4 points.
stroke 4 JoinRound (CapRound, CapRound) $
[CubicBezierPrim $ CubicBezier (V2 0 10) (V2 205 250)
(V2 (-10) 250) (V2 160 35)]

Constructors
| CubicBezier | |
Fields
| |
Describe a simple 2D line between two points.
fill $ LinePrim <$> [ Line (V2 10 10) (V2 190 10)
, Line (V2 190 10) (V2 95 170)
, Line (V2 95 170) (V2 10 10)]
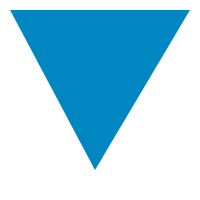
Instances
Describe a quadratic bezier spline, described using 3 points.
fill $ BezierPrim <$> [Bezier (V2 10 10) (V2 200 50) (V2 200 100)
,Bezier (V2 200 100) (V2 150 200) (V2 120 175)
,Bezier (V2 120 175) (V2 30 100) (V2 10 10)]
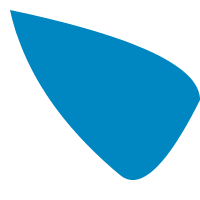
Constructors
| Bezier | |
Instances
This datatype gather all the renderable primitives, they are kept separated otherwise to allow specialization on some specific algorithms. You can mix the different primitives in a single call :
fill
[ CubicBezierPrim $ CubicBezier (V2 50 20) (V2 90 60)
(V2 5 100) (V2 50 140)
, LinePrim $ Line (V2 50 140) (V2 120 80)
, LinePrim $ Line (V2 120 80) (V2 50 20) ]

Constructors
| LinePrim !Line | Primitive used for lines |
| BezierPrim !Bezier | Primitive used for quadratic beziers curves |
| CubicBezierPrim !CubicBezier | Primitive used for cubic bezier curve |
Describe a path in a way similar to many graphical packages, using a "pen" position in memory and reusing it for the next "move" For example the example from Primitive could be rewritten:
fill . pathToPrimitives $ Path (V2 50 20) True [ PathCubicBezierCurveTo (V2 90 60) (V2 5 100) (V2 50 140) , PathLineTo (V2 120 80) ]

Constructors
| Path | |
Fields
| |
Instances
data PathCommand Source
Actions to create a path
Constructors
| PathLineTo Point | Draw a line from the current point to another point |
| PathQuadraticBezierCurveTo Point Point | Draw a quadratic bezier curve from the current point through the control point to the end point. |
| PathCubicBezierCurveTo Point Point Point | Draw a cubic bezier curve using 2 control points. |
class Transformable a where Source
This typeclass is there to help transform the geometry, by applying a transformation on every point of a geometric element.
class PointFoldable a where Source
Typeclass helper gathering all the points of a given geometry.
Methods
foldPoints :: (b -> Point -> b) -> b -> a -> b Source
Fold an accumulator on all the points of the primitive.
Helpers
line :: Point -> Point -> [Primitive] Source
Return a simple line ready to be stroked.
stroke 17 JoinRound (CapRound, CapRound) $
line (V2 10 10) (V2 180 170)
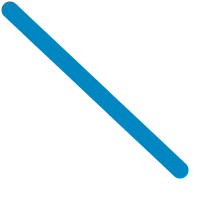
Generate a list of primitive representing a rectangle
fill $ rectangle (V2 30 30) 150 100

Arguments
| :: Point | Corner upper left |
| -> Float | Width in pixel |
| -> Float | Height in pixel. |
| -> Float | Radius along the x axis of the rounded corner. In pixel. |
| -> Float | Radius along the y axis of the rounded corner. In pixel. |
| -> [Primitive] |
Generate a list of primitive representing a rectangle with rounded corner.
fill $ roundedRectangle (V2 10 10) 150 150 20 10

Generate a list of primitive representing a circle.
fill $ circle (V2 100 100) 75

ellipse :: Point -> Float -> Float -> [Primitive] Source
Generate a list of primitive representing an ellipse.
fill $ ellipse (V2 100 100) 75 30
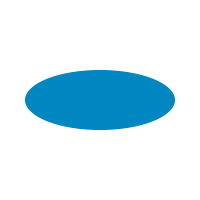
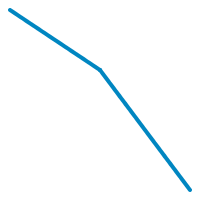
polyline :: [Point] -> [Primitive] Source
Generate a strokable line out of points list.
Just an helper around lineFromPath.
stroke 4 JoinRound (CapRound, CapRound) $ polyline [V2 10 10, V2 100 70, V2 190 190]
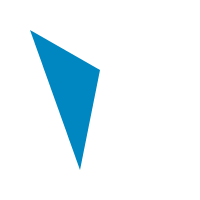
polygon :: [Point] -> [Primitive] Source
Generate a fillable polygon out of points list.
Similar to the polyline function, but close the
path.
fill $ polygon [V2 30 30, V2 100 70, V2 80 170]
Arguments
| :: (Pixel px, Modulable (PixelBaseComponent px)) | |
| => Image px | Image to be drawn |
| -> StrokeWidth | Border size, drawn with current texture. |
| -> Point | Position of the corner upper left of the image. |
| -> Float | Width of the drawn image |
| -> Float | Height of the drawn image |
| -> Drawing px () |
Draw an image with the desired size
drawImageAtSize textureImage 2 (V2 30 30) 128 128

Arguments
| :: (Pixel px, Modulable (PixelBaseComponent px)) | |
| => Image px | Image to be drawn |
| -> StrokeWidth | Border size, drawn with current texture. |
| -> Point | Position of the corner upper left of the image. |
| -> Drawing px () |
Simply draw an image into the canvas. Take into account any previous transformation performed on the geometry.
drawImage textureImage 0 (V2 30 30)

Geometry Helpers
Arguments
| :: Point | Minimum point (corner upper left) |
| -> Point | Maximum point (corner bottom right) |
| -> Primitive | Primitive to be clipped |
| -> [Primitive] |
Clip the geometry to a rectangle.
bezierFromPath :: [Point] -> [Bezier] Source
Create a list of bezier patch from a list of points,
bezierFromPath [a, b, c, d, e] == [Bezier a b c, Bezier c d e]
bezierFromPath [a, b, c, d, e, f] == [Bezier a b c, Bezier c d e]
bezierFromPath [a, b, c, d, e, f, g] ==
[Bezier a b c, Bezier c d e, Bezier e f g]
lineFromPath :: [Point] -> [Line] Source
Transform a list a point to a list of lines
lineFromPath [a, b, c, d] = [Line a b, Line b c, Line c d]
cubicBezierFromPath :: [Point] -> [CubicBezier] Source
Create a list of cubic bezier patch from a list of points.
cubicBezierFromPath [a, b, c, d, e] = [CubicBezier a b c d] cubicBezierFromPath [a, b, c, d, e, f, g] = [CubicBezier a b c d, CubicBezier d e f g]
Rasterization control
Describe how to display the join of broken lines while stroking.
Describe how we will "finish" the stroking that don't loop.
Constructors
| CapStraight Float | Create a straight caping on the stroke. Cap value should be positive and represent the distance from the end of curve to the actual cap
|
| CapRound | Create a rounded caping on the stroke.
|
data SamplerRepeat Source
Describe the behaviour of samplers and texturers when they are out of the bounds of image and/or gradient.
Constructors
| SamplerPad | Will clamp (ie. repeat the last pixel) when
out of bound
|
| SamplerRepeat | Will loop on it's definition domain
|
| SamplerReflect | Will loop inverting axises
|
Instances
data FillMethod Source
Tell how to fill complex shapes when there is self
intersections. If the filling mode is not specified,
then it's the FillWinding method which is used.
The examples used are produced with the following function:
fillingSample :: FillMethod -> Drawing px ()
fillingSample fillMethod = fillWithMethod fillMethod geometry where
geometry = transform (applyTransformation $ scale 0.35 0.4
<> translate (V2 (-80) (-180)))
$ concatMap pathToPrimitives
[ Path (V2 484 499) True
[ PathCubicBezierCurveTo (V2 681 452) (V2 639 312) (V2 541 314)
, PathCubicBezierCurveTo (V2 327 337) (V2 224 562) (V2 484 499)
]
, Path (V2 136 377) True
[ PathCubicBezierCurveTo (V2 244 253) (V2 424 420) (V2 357 489)
, PathCubicBezierCurveTo (V2 302 582) (V2 47 481) (V2 136 377)
]
, Path (V2 340 265) True
[ PathCubicBezierCurveTo (V2 64 371) (V2 128 748) (V2 343 536)
, PathCubicBezierCurveTo (V2 668 216) (V2 17 273) (V2 367 575)
, PathCubicBezierCurveTo (V2 589 727) (V2 615 159) (V2 340 265)
]
]
Constructors
| FillWinding | Also known as nonzero rule. To determine if a point falls inside the curve, you draw an imaginary line through that point. Next you will count how many times that line crosses the curve before it reaches that point. For every clockwise rotation, you subtract 1 and for every counter-clockwise rotation you add 1.
|
| FillEvenOdd | This rule determines the insideness of a point on the canvas by drawing a ray from that point to infinity in any direction and counting the number of path segments from the given shape that the ray crosses. If this number is odd, the point is inside; if even, the point is outside.
|
Instances
type DashPattern = [Float] Source
Dash pattern to use
Debugging helper
dumpDrawing :: Show px => Drawing px () -> String Source
This function will spit out drawing instructions to help debugging.
The outputted code looks like Haskell, but there is no guarantee that it is compilable.