| Copyright | Will Thompson and Iñaki García Etxebarria |
|---|---|
| License | LGPL-2.1 |
| Maintainer | Iñaki García Etxebarria |
| Safe Haskell | Safe-Inferred |
| Language | Haskell2010 |
GI.Gtk.Objects.MessageDialog
Description
GtkMessageDialog presents a dialog with some message text.
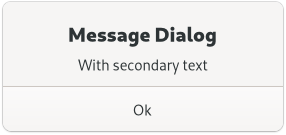
It’s simply a convenience widget; you could construct the equivalent of
GtkMessageDialog from GtkDialog without too much effort, but
GtkMessageDialog saves typing.
The easiest way to do a modal message dialog is to use the DialogFlagsModal
flag, which will call windowSetModal internally. The dialog will
prevent interaction with the parent window until it's hidden or destroyed.
You can use the Dialog::response signal to know when the user
dismissed the dialog.
An example for using a modal dialog:
c code
GtkDialogFlags flags = GTK_DIALOG_DESTROY_WITH_PARENT | GTK_DIALOG_MODAL;
dialog = gtk_message_dialog_new (parent_window,
flags,
GTK_MESSAGE_ERROR,
GTK_BUTTONS_CLOSE,
"Error reading “%s”: %s",
filename,
g_strerror (errno));
// Destroy the dialog when the user responds to it
// (e.g. clicks a button)
g_signal_connect (dialog, "response",
G_CALLBACK (gtk_window_destroy),
NULL);You might do a non-modal GtkMessageDialog simply by omitting the
DialogFlagsModal flag:
c code
GtkDialogFlags flags = GTK_DIALOG_DESTROY_WITH_PARENT;
dialog = gtk_message_dialog_new (parent_window,
flags,
GTK_MESSAGE_ERROR,
GTK_BUTTONS_CLOSE,
"Error reading “%s”: %s",
filename,
g_strerror (errno));
// Destroy the dialog when the user responds to it
// (e.g. clicks a button)
g_signal_connect (dialog, "response",
G_CALLBACK (gtk_window_destroy),
NULL);GtkMessageDialog as GtkBuildable
The GtkMessageDialog implementation of the GtkBuildable interface exposes
the message area as an internal child with the name “message_area”.
Synopsis
- newtype MessageDialog = MessageDialog (ManagedPtr MessageDialog)
- class (GObject o, IsDescendantOf MessageDialog o) => IsMessageDialog o
- toMessageDialog :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> m MessageDialog
- messageDialogGetMessageArea :: (HasCallStack, MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog a) => a -> m Widget
- messageDialogSetMarkup :: (HasCallStack, MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog a) => a -> Text -> m ()
- constructMessageDialogButtons :: (IsMessageDialog o, MonadIO m) => ButtonsType -> m (GValueConstruct o)
- getMessageDialogMessageArea :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> m Widget
- constructMessageDialogMessageType :: (IsMessageDialog o, MonadIO m) => MessageType -> m (GValueConstruct o)
- getMessageDialogMessageType :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> m MessageType
- setMessageDialogMessageType :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> MessageType -> m ()
- clearMessageDialogSecondaryText :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> m ()
- constructMessageDialogSecondaryText :: (IsMessageDialog o, MonadIO m) => Text -> m (GValueConstruct o)
- getMessageDialogSecondaryText :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> m (Maybe Text)
- setMessageDialogSecondaryText :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> Text -> m ()
- constructMessageDialogSecondaryUseMarkup :: (IsMessageDialog o, MonadIO m) => Bool -> m (GValueConstruct o)
- getMessageDialogSecondaryUseMarkup :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> m Bool
- setMessageDialogSecondaryUseMarkup :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> Bool -> m ()
- clearMessageDialogText :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> m ()
- constructMessageDialogText :: (IsMessageDialog o, MonadIO m) => Text -> m (GValueConstruct o)
- getMessageDialogText :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> m (Maybe Text)
- setMessageDialogText :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> Text -> m ()
- constructMessageDialogUseMarkup :: (IsMessageDialog o, MonadIO m) => Bool -> m (GValueConstruct o)
- getMessageDialogUseMarkup :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> m Bool
- setMessageDialogUseMarkup :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> Bool -> m ()
Exported types
newtype MessageDialog Source #
Memory-managed wrapper type.
Constructors
| MessageDialog (ManagedPtr MessageDialog) |
Instances
class (GObject o, IsDescendantOf MessageDialog o) => IsMessageDialog o Source #
Type class for types which can be safely cast to MessageDialog, for instance with toMessageDialog.
Instances
| (GObject o, IsDescendantOf MessageDialog o) => IsMessageDialog o Source # | |
Defined in GI.Gtk.Objects.MessageDialog | |
toMessageDialog :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> m MessageDialog Source #
Cast to MessageDialog, for types for which this is known to be safe. For general casts, use castTo.
Methods
Click to display all available methods, including inherited ones
Methods
actionSetEnabled, activate, activateAction, activateDefault, addActionWidget, addButton, addController, addCssClass, addMnemonicLabel, addTickCallback, allocate, bindProperty, bindPropertyFull, childFocus, close, computeBounds, computeExpand, computePoint, computeTransform, contains, createPangoContext, createPangoLayout, destroy, disposeTemplate, dragCheckThreshold, errorBell, forceFloating, freezeNotify, fullscreen, fullscreenOnMonitor, getv, grabFocus, hasCssClass, hasDefault, hasFocus, hasGroup, hasVisibleFocus, hide, inDestruction, initTemplate, insertActionGroup, insertAfter, insertBefore, isActive, isAncestor, isDrawable, isFloating, isFocus, isFullscreen, isMaximized, isSensitive, isVisible, keynavFailed, listMnemonicLabels, map, maximize, measure, minimize, mnemonicActivate, notify, notifyByPspec, observeChildren, observeControllers, pick, present, presentWithTime, queueAllocate, queueDraw, queueResize, realize, ref, refSink, removeController, removeCssClass, removeMnemonicLabel, removeTickCallback, resetProperty, resetRelation, resetState, response, runDispose, shouldLayout, show, sizeAllocate, snapshotChild, stealData, stealQdata, thawNotify, translateCoordinates, triggerTooltipQuery, unfullscreen, unmap, unmaximize, unminimize, unparent, unrealize, unref, unsetStateFlags, updateProperty, updateRelation, updateState, watchClosure.
Getters
getAccessibleRole, getAllocatedBaseline, getAllocatedHeight, getAllocatedWidth, getAllocation, getAncestor, getApplication, getBuildableId, getCanFocus, getCanTarget, getChild, getChildVisible, getClipboard, getContentArea, getCssClasses, getCssName, getCursor, getData, getDecorated, getDefaultSize, getDefaultWidget, getDeletable, getDestroyWithParent, getDirection, getDisplay, getFirstChild, getFocus, getFocusChild, getFocusOnClick, getFocusVisible, getFocusable, getFontMap, getFontOptions, getFrameClock, getGroup, getHalign, getHandleMenubarAccel, getHasTooltip, getHeaderBar, getHeight, getHexpand, getHexpandSet, getHideOnClose, getIconName, getLastChild, getLayoutManager, getMapped, getMarginBottom, getMarginEnd, getMarginStart, getMarginTop, getMessageArea, getMnemonicsVisible, getModal, getName, getNative, getNextSibling, getOpacity, getOverflow, getPangoContext, getParent, getPreferredSize, getPrevSibling, getPrimaryClipboard, getProperty, getQdata, getRealized, getReceivesDefault, getRenderer, getRequestMode, getResizable, getResponseForWidget, getRoot, getScaleFactor, getSensitive, getSettings, getSize, getSizeRequest, getStateFlags, getStyleContext, getSurface, getSurfaceTransform, getTemplateChild, getTitle, getTitlebar, getTooltipMarkup, getTooltipText, getTransientFor, getValign, getVexpand, getVexpandSet, getVisible, getWidgetForResponse, getWidth.
Setters
setApplication, setCanFocus, setCanTarget, setChild, setChildVisible, setCssClasses, setCursor, setCursorFromName, setData, setDataFull, setDecorated, setDefaultResponse, setDefaultSize, setDefaultWidget, setDeletable, setDestroyWithParent, setDirection, setDisplay, setFocus, setFocusChild, setFocusOnClick, setFocusVisible, setFocusable, setFontMap, setFontOptions, setHalign, setHandleMenubarAccel, setHasTooltip, setHexpand, setHexpandSet, setHideOnClose, setIconName, setLayoutManager, setMarginBottom, setMarginEnd, setMarginStart, setMarginTop, setMarkup, setMnemonicsVisible, setModal, setName, setOpacity, setOverflow, setParent, setProperty, setReceivesDefault, setResizable, setResponseSensitive, setSensitive, setSizeRequest, setStartupId, setStateFlags, setTitle, setTitlebar, setTooltipMarkup, setTooltipText, setTransientFor, setValign, setVexpand, setVexpandSet, setVisible.
getMessageArea
messageDialogGetMessageArea Source #
Arguments
| :: (HasCallStack, MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog a) | |
| => a |
|
| -> m Widget | Returns: A |
Returns the message area of the dialog.
This is the box where the dialog’s primary and secondary labels
are packed. You can add your own extra content to that box and it
will appear below those labels. See dialogGetContentArea
for the corresponding function in the parent Dialog.
setMarkup
messageDialogSetMarkup Source #
Arguments
| :: (HasCallStack, MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog a) | |
| => a |
|
| -> Text |
|
| -> m () |
Sets the text of the message dialog.
Properties
buttons
No description available in the introspection data.
constructMessageDialogButtons :: (IsMessageDialog o, MonadIO m) => ButtonsType -> m (GValueConstruct o) Source #
Construct a GValueConstruct with valid value for the “buttons” property. This is rarely needed directly, but it is used by new.
messageArea
The GtkBox that corresponds to the message area of this dialog.
See messageDialogGetMessageArea for a detailed
description of this area.
getMessageDialogMessageArea :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> m Widget Source #
Get the value of the “message-area” property.
When overloading is enabled, this is equivalent to
get messageDialog #messageArea
messageType
The type of the message.
constructMessageDialogMessageType :: (IsMessageDialog o, MonadIO m) => MessageType -> m (GValueConstruct o) Source #
Construct a GValueConstruct with valid value for the “message-type” property. This is rarely needed directly, but it is used by new.
getMessageDialogMessageType :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> m MessageType Source #
Get the value of the “message-type” property.
When overloading is enabled, this is equivalent to
get messageDialog #messageType
setMessageDialogMessageType :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> MessageType -> m () Source #
Set the value of the “message-type” property.
When overloading is enabled, this is equivalent to
setmessageDialog [ #messageType:=value ]
secondaryText
The secondary text of the message dialog.
clearMessageDialogSecondaryText :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> m () Source #
Set the value of the “secondary-text” property to Nothing.
When overloading is enabled, this is equivalent to
clear #secondaryText
constructMessageDialogSecondaryText :: (IsMessageDialog o, MonadIO m) => Text -> m (GValueConstruct o) Source #
Construct a GValueConstruct with valid value for the “secondary-text” property. This is rarely needed directly, but it is used by new.
getMessageDialogSecondaryText :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> m (Maybe Text) Source #
Get the value of the “secondary-text” property.
When overloading is enabled, this is equivalent to
get messageDialog #secondaryText
setMessageDialogSecondaryText :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> Text -> m () Source #
Set the value of the “secondary-text” property.
When overloading is enabled, this is equivalent to
setmessageDialog [ #secondaryText:=value ]
secondaryUseMarkup
True if the secondary text of the dialog includes Pango markup.
See parseMarkup.
constructMessageDialogSecondaryUseMarkup :: (IsMessageDialog o, MonadIO m) => Bool -> m (GValueConstruct o) Source #
Construct a GValueConstruct with valid value for the “secondary-use-markup” property. This is rarely needed directly, but it is used by new.
getMessageDialogSecondaryUseMarkup :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> m Bool Source #
Get the value of the “secondary-use-markup” property.
When overloading is enabled, this is equivalent to
get messageDialog #secondaryUseMarkup
setMessageDialogSecondaryUseMarkup :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> Bool -> m () Source #
Set the value of the “secondary-use-markup” property.
When overloading is enabled, this is equivalent to
setmessageDialog [ #secondaryUseMarkup:=value ]
text
The primary text of the message dialog.
If the dialog has a secondary text, this will appear as the title.
clearMessageDialogText :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> m () Source #
Set the value of the “text” property to Nothing.
When overloading is enabled, this is equivalent to
clear #text
constructMessageDialogText :: (IsMessageDialog o, MonadIO m) => Text -> m (GValueConstruct o) Source #
Construct a GValueConstruct with valid value for the “text” property. This is rarely needed directly, but it is used by new.
getMessageDialogText :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> m (Maybe Text) Source #
Get the value of the “text” property.
When overloading is enabled, this is equivalent to
get messageDialog #text
setMessageDialogText :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> Text -> m () Source #
Set the value of the “text” property.
When overloading is enabled, this is equivalent to
setmessageDialog [ #text:=value ]
useMarkup
True if the primary text of the dialog includes Pango markup.
See parseMarkup.
constructMessageDialogUseMarkup :: (IsMessageDialog o, MonadIO m) => Bool -> m (GValueConstruct o) Source #
Construct a GValueConstruct with valid value for the “use-markup” property. This is rarely needed directly, but it is used by new.
getMessageDialogUseMarkup :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> m Bool Source #
Get the value of the “use-markup” property.
When overloading is enabled, this is equivalent to
get messageDialog #useMarkup
setMessageDialogUseMarkup :: (MonadIO m, IsMessageDialog o) => o -> Bool -> m () Source #
Set the value of the “use-markup” property.
When overloading is enabled, this is equivalent to
setmessageDialog [ #useMarkup:=value ]