| Copyright | (c) Justus Sagemüller 2015 |
|---|---|
| License | GPL v3 |
| Maintainer | (@) sagemueller $ geo.uni-koeln.de |
| Stability | experimental |
| Portability | portable |
| Safe Haskell | None |
| Language | Haskell2010 |
Data.Manifold.TreeCover
Description
- data Shade x
- shadeCtr :: Shade x -> x
- shadeExpanse :: Shade x -> Metric' x
- fullShade :: WithField ℝ Manifold x => x -> Metric' x -> Shade x
- pointsShades :: WithField ℝ Manifold x => [x] -> [Shade x]
- data ShadeTree x
- = PlainLeaves [x]
- | DisjointBranches !Int (NonEmpty (ShadeTree x))
- | OverlappingBranches !Int !(Shade x) (NonEmpty (DBranch x))
- fromLeafPoints :: forall x. WithField ℝ Manifold x => [x] -> ShadeTree x
- onlyNodes :: WithField ℝ Manifold x => ShadeTree x -> Trees x
- onlyLeaves :: WithField ℝ Manifold x => ShadeTree x -> [x]
- type SimpleTree = GenericTree Maybe []
- type Trees = GenericTree [] []
- type NonEmptyTree = GenericTree NonEmpty []
- newtype GenericTree c b x = GenericTree {
- treeBranches :: c (x, GenericTree b b x)
- sShSaw :: WithField ℝ Manifold x => ShadeTree x -> ShadeTree x -> Sawboneses x
- chainsaw :: WithField ℝ Manifold x => Cutplane x -> ShadeTree x -> Sawbones x
- class HasFlatView f where
- type FlatView f x
- flatView :: f x -> FlatView f x
- superFlatView :: f x -> [[x]]
- type TriangBuild t n x = TriangT t (S n) x (State (Map (SimplexIT t n x) (Metric x, ISimplex (S n) x)))
- doTriangBuild :: KnownNat n => (forall t. TriangBuild t n x ()) -> [Simplex (S n) x]
- singleFullSimplex :: forall t n x. (KnownNat n, WithField ℝ Manifold x) => ISimplex n x -> FullTriang t n x (SimplexIT t n x)
- autoglueTriangulation :: forall t n n' n'' x. (KnownNat n'', WithField ℝ Manifold x, n ~ S n', n' ~ S n'') => (forall t'. TriangBuild t' n' x ()) -> TriangBuild t n' x ()
- data AutoTriang n x
- elementaryTriang :: forall n n' x. (KnownNat n', n ~ S n', WithField ℝ EuclidSpace x) => Simplex n x -> AutoTriang n x
- breakdownAutoTriang :: forall n n' x. (KnownNat n', n ~ S n') => AutoTriang n x -> [Simplex n x]
Shades
A Shade is a very crude description of a region within a manifold. It
can be interpreted as either an ellipsoid shape, or as the Gaussian peak
of a normal distribution (use http://hackage.haskell.org/package/manifold-random
for actually sampling from that distribution).
For a precise description of an arbitrarily-shaped connected subset of a manifold,
there is Region, whose implementation is vastly more complex.
Instances
| AffineManifold x => Semimanifold (Shade x) | |
| type Needle (Shade x) = Diff x |
shadeExpanse :: Shade x -> Metric' x Source
pointsShades :: WithField ℝ Manifold x => [x] -> [Shade x] Source
Attempt to find a Shade that “covers” the given points.
At least in an affine space (and thus locally in any manifold), this can be used to
estimate the parameters of a normal distribution from which some points were
sampled.
For nonconnected manifolds it will be necessary to yield separate shades for each connected component. And for an empty input list, there is no shade! Hence the list result.
Shade trees
Constructors
| PlainLeaves [x] | |
| DisjointBranches !Int (NonEmpty (ShadeTree x)) | |
| OverlappingBranches !Int !(Shade x) (NonEmpty (DBranch x)) |
Instances
| Generic (ShadeTree x) | |
| WithField ℝ Manifold x => Monoid (ShadeTree x) | |
| (NFData x, NFData (DualSpace (Needle x))) => NFData (ShadeTree x) | |
| WithField ℝ Manifold x => Semigroup (ShadeTree x) | WRT union. |
| AffineManifold x => Semimanifold (ShadeTree x) | Experimental. There might be a more powerful instance possible. |
| type Rep (ShadeTree x) | |
| type Needle (ShadeTree x) = Diff x |
fromLeafPoints :: forall x. WithField ℝ Manifold x => [x] -> ShadeTree x Source
Build a really quite nicely balanced tree from a cloud of points, on any real manifold.
Example:
> :m +Graphics.Dynamic.Plot.R2 Data.Manifold.TreeCover Data.VectorSpace Data.AffineSpace
> import Diagrams.Prelude ((^&), P2, R2, circle, fc, (&), moveTo, green)
> let testPts0 = [0^&0, 0^&1, 1^&1, 1^&2, 2^&2] :: [P2] -- Generate sort-of–random point cloud
> let testPts1 = [p .+^ v^/3 | p<-testPts0, v <- [0^&0, (-1)^&1, 1^&2]]
> let testPts2 = [p .+^ v^/4 | p<-testPts1, v <- [0^&0, (-1)^&1, 1^&2]]
> let testPts3 = [p .+^ v^/5 | p<-testPts2, v <- [0^&0, (-2)^&1, 1^&2]]
> let testPts4 = [p .+^ v^/7 | p<-testPts3, v <- [0^&1, (-2)^&1, 1^&2]]
> length testPts4
405
> plotWindow [ plot . onlyNodes $ fromLeafPoints testPts4
> , plot [circle 0.06 & moveTo p & fc green :: PlainGraphics | p <- testPts4] ]
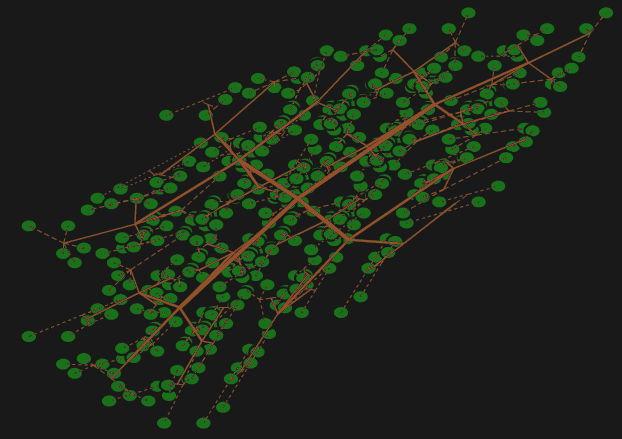
Simple view helpers
onlyNodes :: WithField ℝ Manifold x => ShadeTree x -> Trees x Source
Imitate the specialised ShadeTree structure with a simpler, generic tree.
onlyLeaves :: WithField ℝ Manifold x => ShadeTree x -> [x] Source
Left (and, typically, also right) inverse of fromLeafNodes.
Auxiliary types
type SimpleTree = GenericTree Maybe [] Source
SimpleTreex ≅ Maybe (x,Treesx)
type Trees = GenericTree [] [] Source
type NonEmptyTree = GenericTree NonEmpty [] Source
NonEmptyTreex ≅ (x,Treesx)
newtype GenericTree c b x Source
Constructors
| GenericTree | |
Fields
| |
Instances
| (Functor c, Functor b) => Functor (GenericTree c b) | |
| Show (c (x, GenericTree b b x)) => Show (GenericTree c b x) | |
| MonadPlus c => Monoid (GenericTree c b x) | |
| MonadPlus c => Semigroup (GenericTree c b x) |
Misc
Arguments
| :: WithField ℝ Manifold x | |
| => ShadeTree x | “Reference tree”, defines the cut regions.
Must be at least one level of |
| -> ShadeTree x | Tree to take the actual contents from. |
| -> Sawboneses x | All points within each region, plus those from the boundaries of each neighbouring region. |
Saw a tree into the domains covered by the respective branches of another tree.
class HasFlatView f where Source
Triangulation-builders
type TriangBuild t n x = TriangT t (S n) x (State (Map (SimplexIT t n x) (Metric x, ISimplex (S n) x))) Source
doTriangBuild :: KnownNat n => (forall t. TriangBuild t n x ()) -> [Simplex (S n) x] Source
singleFullSimplex :: forall t n x. (KnownNat n, WithField ℝ Manifold x) => ISimplex n x -> FullTriang t n x (SimplexIT t n x) Source
autoglueTriangulation :: forall t n n' n'' x. (KnownNat n'', WithField ℝ Manifold x, n ~ S n', n' ~ S n'') => (forall t'. TriangBuild t' n' x ()) -> TriangBuild t n' x () Source
BUGGY: this does connect the supplied triangulations, but it doesn't choose the right boundary simplices yet. Probable cause: inconsistent internal numbering of the subsimplices.
data AutoTriang n x Source
elementaryTriang :: forall n n' x. (KnownNat n', n ~ S n', WithField ℝ EuclidSpace x) => Simplex n x -> AutoTriang n x Source
breakdownAutoTriang :: forall n n' x. (KnownNat n', n ~ S n') => AutoTriang n x -> [Simplex n x] Source