| Copyright | Marco Zocca 2017 |
|---|---|
| License | BSD3 |
| Maintainer | Marco Zocca <zocca marco gmail> |
| Safe Haskell | None |
| Language | Haskell2010 |
Graphics.Rendering.Plot.Light
Contents
Description
plot-light provides functionality for rendering vector
graphics in SVG format. It is geared in particular towards scientific plotting, and it is termed "light" because it only requires a few common Haskell dependencies and no external libraries.
Usage
To incorporate this library in your projects you just need import Graphics.Rendering.Plot.Light. If GHC complains of name collisions you must import the module in "qualified" form.
Examples
If you wish to try out the examples in this page, you will need to have these import statements as well :
import Text.Blaze.Svg.Renderer.String (renderSvg) import qualified Data.Colour.Names as C import qualified Data.Text.IO as T (readFile, writeFile) import qualified Data.Text as T
1. Heatmap plot of a 2D function
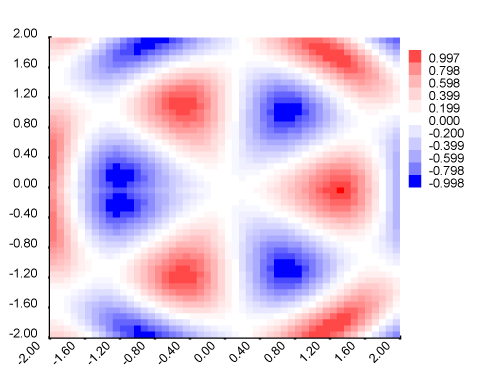
This example renders the function
\[ {f(x, y) = \cos(\pi \theta) \sin( \rho^2) } \] where \( \rho^2 = x^2 + y^2 \) and \( \theta = \arctan(y/x) \).
xPlot = 400
yPlot = 300
fdat = FigureData xPlot yPlot 0.1 0.8 0.1 0.9 10
palette0 = palette [C.red, C.white, C.blue] 15
plotFun2ex1 = do
let
p1 = Point (-2) (-2)
p2 = Point 2 2
frame = mkFrame p1 p2
nx = 50
ny = 50
f x y = cos ( pi * theta ) * sin r
where
r = x'**2 + y'**2
theta = atan2 y' x'
(x', y') = (fromRational x, fromRational y)
lps = plotFun2 f $ meshGrid frame nx ny
vmin = minimum $ _lplabel <$> lps
vmax = maximum $ _lplabel <$> lps
pixels = heatmap' fdat palette0 frame nx ny lps
cbar = colourBar fdat palette0 10 vmin vmax 10 TopRight 100
svg_t = svgHeader xPlot yPlot $ do
axes fdat frame 2 C.black 10 10
pixels
cbar
T.writeFile "heatmap.svg" $ T.pack $ renderSvg svg_tThis example demonstrates how to plot a 2D scalar function and write the output to SVG file.
First, we define a FigureData object (which holds the SVG figure dimensions and parameters for the white margin around the rendering canvas) and a palette.
Afterwards we declare a Frame that bounds the rendering canvas using mkFrame. This is discretized in nx by ny pixels with meshGrid, and the function f is computed at the intersections of the mesh with plotFun2.
The axes function adds labeled axes to the figure; the user just needs to specify stroke width and color and how many ticks to display.
The data to be plotted (represented in this case as a list of LabeledPoints, in which the "label" carries the function value) are then mapped onto the given colour palette and drawn to the SVG canvas as a heatmap', i.e. a mesh of filled rectangles (Caution: do not exceed resolutions of ~ hundred pixels per side).
Next, we create the legend; in this case this is a colourBar element that requires the data bounds vmin, vmax.
As a last step, the SVG content is wrapped in the appropriate markdown by svgHeader and written to file.
2. Scatter plot of 3D data
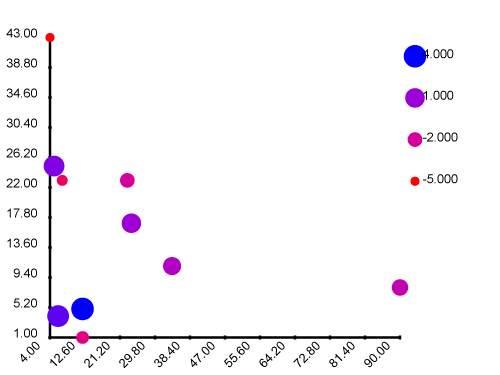
This example shows how to plot a collection of labelled points in the plane. Each sample row is represented by a LabeledPoint, in which the label is a scalar quantity.
The scatterLP function renders each data row as a glyph, by modifying a ScatterPointData record of default values via three functions that control the glyph size, contour line thickness and colour. This functionality can be exploited in creative ways to achieve effective infographics.
xPlot = 400
yPlot = 300
fnameOut = "data/scatter-1.svg"
fdat = FigureData xPlot yPlot 0.1 0.8 0.1 0.9 10
dats = zipWith LabeledPoint p_ l_ where
l_ = [-5, -4 .. ]
p_ = zipWith Point [4,7,12,23,90,34,24,5,6,12,3] [43,23,1,23,8,11,17,25,4,5]
spdata = ScatterPointData Circle 3 3 C.red
main = do
let
frameTo = frameFromFigData fdat
frameFrom = frameFromPoints $ _lp <$> dats
vmin = minimum $ _lplabel <$> dats
vmax = maximum $ _lplabel <$> dats
f l sz = 10/(1 + exp(-(0.3 * x)))
where x = l + sz
g _ w = w
h l col = C.blend l' C.blue col
where
l' = (l - vmin)/(vmax - vmin)
dats' = moveLabeledPointBwFrames frameFrom frameTo False True <$> dats
svg_t = svgHeader xPlot yPlot $ do
axes fdat frameFrom 2 C.black 10 10
scatterLP f g h spdata dats'
scatterLPBar fdat 50 vmin vmax 3 TopRight 100 f g h spdata
T.writeFile fnameOut $ T.pack $ renderSvg svg_t- heatmap :: FigureData Rational -> [Colour Double] -> [[Scientific]] -> Svg
- heatmap' :: (Foldable f, Functor f, Show a, RealFrac a, RealFrac t) => FigureData a -> [Colour Double] -> Frame a -> a -> a -> f (LabeledPoint t a) -> Svg
- plotFun2 :: Functor f => (t -> t -> l) -> f (Point t) -> f (LabeledPoint l t)
- colourBar :: (RealFrac t, RealFrac a, Show a, Enum t, Floating a) => FigureData (Ratio Integer) -> [Colour Double] -> a -> t -> t -> Int -> LegendPosition_ -> a -> Svg
- scatter :: (Foldable t, Show a, RealFrac a) => ScatterPointData a -> t (Point a) -> Svg
- scatterLP :: (Foldable t, RealFrac a, Show a) => (l -> b -> a) -> (l -> b -> a) -> (l -> Colour Double -> Colour Double) -> ScatterPointData b -> t (LabeledPoint l a) -> Svg
- scatterLPBar :: (RealFrac t, Enum t, RealFrac b, Show b) => FigureData b -> b -> t -> t -> Int -> LegendPosition_ -> b -> (t -> b -> b) -> (t -> b -> b) -> (t -> Colour Double -> Colour Double) -> ScatterPointData b -> Svg
- data ScatterPointData a = ScatterPointData {
- spGlyphShape :: GlyphShape_
- spSize :: a
- spStrokeWidth :: a
- spColour :: Colour Double
- data GlyphShape_
- rect :: (Show a, RealFrac a) => a -> a -> a -> Maybe (Colour Double) -> Maybe (Colour Double) -> Point a -> Svg
- rectCentered :: (Show a, RealFrac a) => a -> a -> a -> Maybe (Colour Double) -> Maybe (Colour Double) -> Point a -> Svg
- squareCentered :: (Show a, RealFrac a) => a -> a -> Maybe (Colour Double) -> Maybe (Colour Double) -> Point a -> Svg
- circle :: (Real a1, Real a) => a -> a -> Maybe (Colour Double) -> Maybe (Colour Double) -> Point a1 -> Svg
- line :: (Show a, RealFrac a) => Point a -> Point a -> a -> LineStroke_ a -> Colour Double -> Svg
- text :: (Show a, Real a) => a -> Int -> Colour Double -> TextAnchor_ -> Text -> V2 a -> Point a -> Svg
- polyline :: (Foldable t, Show a1, Show a, RealFrac a, RealFrac a1) => a1 -> LineStroke_ a -> StrokeLineJoin_ -> Colour Double -> t (Point a) -> Svg
- filledPolyline :: (Foldable t, Show a, Real o) => Colour Double -> o -> t (Point a) -> Svg
- pixel :: (Show a, RealFrac a) => [Colour Double] -> a -> a -> Scientific -> Scientific -> LabeledPoint Scientific a -> Svg
- pixel' :: (Show a, RealFrac a, RealFrac t) => [Colour Double] -> a -> a -> t -> t -> LabeledPoint t a -> Svg
- filledBand :: (Foldable t, Real o, Show a) => Colour Double -> o -> (l -> a) -> (l -> a) -> t (LabeledPoint l a) -> Svg
- candlestick :: (Show a, RealFrac a) => (a -> a -> Bool) -> (l -> a) -> (l -> a) -> (l -> a) -> (l -> a) -> a -> a -> Colour Double -> Colour Double -> Colour Double -> LabeledPoint l a -> Svg
- axes :: (Show a, RealFrac a) => FigureData a -> Frame a -> a -> Colour Double -> Int -> Int -> Svg
- toPlot :: (Functor t, Foldable t, Show a, RealFrac a) => FigureData a -> (l -> Text) -> (l -> Text) -> a -> a -> a -> Colour Double -> Maybe (t (LabeledPoint l a)) -> Maybe (t (LabeledPoint l a)) -> (t (LabeledPoint l a) -> Svg) -> t (LabeledPoint l a) -> Svg
- data FigureData a = FigureData {
- figWidth :: a
- figHeight :: a
- figLeftMFrac :: a
- figRightMFrac :: a
- figTopMFrac :: a
- figBottomMFrac :: a
- figLabelFontSize :: Int
- data LineStroke_ a
- = Continuous
- | Dashed [a]
- data StrokeLineJoin_
- data TextAnchor_
- data LegendPosition_
- frameFromPoints :: (Ord a, Foldable t, Functor t) => t (Point a) -> Frame a
- frameFromFigData :: Num a => FigureData a -> Frame a
- mkFrame :: Point a -> Point a -> Frame a
- mkFrameOrigin :: Num a => a -> a -> Frame a
- width :: Num a => Frame a -> a
- height :: Num a => Frame a -> a
- figFWidth :: Num a => FigureData a -> a
- figFHeight :: Num a => FigureData a -> a
- blendTwo :: Colour Double -> Colour Double -> Int -> [Colour Double]
- palette :: [Colour Double] -> Int -> [Colour Double]
- pickColour :: RealFrac t => [Colour Double] -> t -> t -> t -> Colour Double
- svgHeader :: Real a => a -> a -> Svg -> Svg
- translateSvg :: Show a => Point a -> Svg -> Svg
- toSvgFrame :: Fractional a => Frame a -> Frame a -> Bool -> Point a -> Point a
- toSvgFrameLP :: Fractional a => Frame a -> Frame a -> Bool -> LabeledPoint l a -> LabeledPoint l a
- data Frame a = Frame {}
- data Point a = Point {}
- data LabeledPoint l a = LabeledPoint {}
- labelPoint :: (Point a -> l) -> Point a -> LabeledPoint l a
- mapLabel :: (l1 -> l2) -> LabeledPoint l1 a -> LabeledPoint l2 a
- data Axis
- meshGrid :: (Enum a, RealFrac a) => Frame a -> Int -> Int -> [Point a]
- toFloat :: Scientific -> Float
- wholeDecimal :: (Integral a, RealFrac b) => b -> (a, b)
Plot types
Heatmap
Arguments
| :: FigureData Rational | Figure data |
| -> [Colour Double] | Colour palette |
| -> [[Scientific]] | Data |
| -> Svg |
Arguments
| :: (Foldable f, Functor f, Show a, RealFrac a, RealFrac t) | |
| => FigureData a | Figure data |
| -> [Colour Double] | Colour palette |
| -> Frame a | Frame containing the data |
| -> a | Number of points along x axis |
| -> a | " y axis |
| -> f (LabeledPoint t a) | Data |
| -> Svg |
heatmap' renders one SVG pixel for every LabeledPoint supplied as input. The LabeledPoints must be bounded by the Frame.
plotFun2 :: Functor f => (t -> t -> l) -> f (Point t) -> f (LabeledPoint l t) Source #
Plot a scalar function f of points in the plane (i.e. \(f : \mathbf{R}^2 \rightarrow \mathbf{R}\))
Arguments
| :: (RealFrac t, RealFrac a, Show a, Enum t, Floating a) | |
| => FigureData (Ratio Integer) | Figure data |
| -> [Colour Double] | Palette |
| -> a | Width |
| -> t | Value range minimum |
| -> t | Value range maximum |
| -> Int | Number of distinct values |
| -> LegendPosition_ | Legend position in the figure |
| -> a | Colour bar length |
| -> Svg |
A colour bar legend, to be used within heatmap-style plots.
Scatter
scatter :: (Foldable t, Show a, RealFrac a) => ScatterPointData a -> t (Point a) -> Svg Source #
Scatter plot
Every point in the plot has the same parameters, as declared in the ScatterPointData record
Arguments
| :: (Foldable t, RealFrac a, Show a) | |
| => (l -> b -> a) | Modifies the glyph size |
| -> (l -> b -> a) | Modifies the glyph stroke width |
| -> (l -> Colour Double -> Colour Double) | Modifies the glyph colour |
| -> ScatterPointData b | Glyph style defaults |
| -> t (LabeledPoint l a) | Data |
| -> Svg |
Parametric scatter plot
The parameters of every point in the scatter plot are modulated according to the label, using the three functions.
This can be used to produce rich infographics, in which e.g. the colour and size of the glyphs carry additional information.
Arguments
| :: (RealFrac t, Enum t, RealFrac b, Show b) | |
| => FigureData b | |
| -> b | Legend width |
| -> t | Data value lower bound |
| -> t | Data value upper bound |
| -> Int | Number of legend entries |
| -> LegendPosition_ | Legend position in the figure |
| -> b | Legend length |
| -> (t -> b -> b) | Modifies the glyph size |
| -> (t -> b -> b) | Modifies the glyph stroke width |
| -> (t -> Colour Double -> Colour Double) | Modifies the glyph colour |
| -> ScatterPointData b | Glyph style defaults |
| -> Svg |
data ScatterPointData a Source #
Parameters for a scatterplot glyph
Constructors
| ScatterPointData | |
Fields
| |
Instances
| Eq a => Eq (ScatterPointData a) Source # | |
| Show a => Show (ScatterPointData a) Source # | |
Plot elements
Geometrical primitives
Arguments
| :: (Show a, RealFrac a) | |
| => a | Width |
| -> a | Height |
| -> a | Stroke width |
| -> Maybe (Colour Double) | Stroke colour |
| -> Maybe (Colour Double) | Fill colour |
| -> Point a | Corner point coordinates |
| -> Svg |
A rectangle, defined by its anchor point coordinates and side lengths
> putStrLn $ renderSvg $ rect (Point 100 200) 30 60 2 Nothing (Just C.aquamarine) <rect x="100.0" y="200.0" width="30.0" height="60.0" fill="#7fffd4" stroke="none" stroke-width="2.0" />
Arguments
| :: (Show a, RealFrac a) | |
| => a | Width |
| -> a | Height |
| -> a | Stroke width |
| -> Maybe (Colour Double) | Stroke colour |
| -> Maybe (Colour Double) | Fill colour |
| -> Point a | Center coordinates |
| -> Svg |
A rectangle, defined by its center coordinates and side lengths
> putStrLn $ renderSvg $ rectCentered 15 30 1 (Just C.blue) (Just C.red) (Point 20 30) <rect x="12.5" y="15.0" width="15.0" height="30.0" fill="#ff0000" stroke="#0000ff" stroke-width="1.0" />
Arguments
| :: (Show a, RealFrac a) | |
| => a | Side length |
| -> a | Stroke width |
| -> Maybe (Colour Double) | Stroke colour |
| -> Maybe (Colour Double) | Fill colour |
| -> Point a | Center coordinates |
| -> Svg |
A square, defined by its center coordinates and side length
Arguments
| :: (Real a1, Real a) | |
| => a | Radius |
| -> a | Stroke width |
| -> Maybe (Colour Double) | Stroke colour |
| -> Maybe (Colour Double) | Fill colour |
| -> Point a1 | Center |
| -> Svg |
A circle
> putStrLn $ renderSvg $ circle (Point 20 30) 15 (Just C.blue) (Just C.red) <circle cx="20.0" cy="30.0" r="15.0" fill="#ff0000" stroke="#0000ff" />
Arguments
| :: (Show a, RealFrac a) | |
| => Point a | First point |
| -> Point a | Second point |
| -> a | Stroke width |
| -> LineStroke_ a | Stroke type |
| -> Colour Double | Stroke colour |
| -> Svg |
Line segment between two Points
> putStrLn $ renderSvg $ line (Point 0 0) (Point 1 1) 0.1 Continuous C.blueviolet <line x1="0.0" y1="0.0" x2="1.0" y2="1.0" stroke="#8a2be2" stroke-width="0.1" />
> putStrLn $ renderSvg (line (Point 0 0) (Point 1 1) 0.1 (Dashed [0.2, 0.3]) C.blueviolet) <line x1="0.0" y1="0.0" x2="1.0" y2="1.0" stroke="#8a2be2" stroke-width="0.1" stroke-dasharray="0.2, 0.3" />
Arguments
| :: (Show a, Real a) | |
| => a | Rotation angle of the textbox |
| -> Int | Font size |
| -> Colour Double | Font colour |
| -> TextAnchor_ | How to anchor the text to the point |
| -> Text | Text |
| -> V2 a | Displacement w.r.t. rotated textbox |
| -> Point a | Initial position of the text box (i.e. before rotation and displacement) |
| -> Svg |
text renders text onto the SVG canvas
Conventions
The Point argument p refers to the lower-left corner of the text box.
The text box can be rotated by rot degrees around p and then anchored at either its beginning, middle or end to p with the TextAnchor_ flag.
The user can supply an additional V2 displacement which will be applied after rotation and anchoring and refers to the rotated text box frame.
> putStrLn $ renderSvg $ text (-45) C.green TAEnd "blah" (V2 (- 10) 0) (Point 250 0) <text x="-10.0" y="0.0" transform="translate(250.0 0.0)rotate(-45.0)" fill="#008000" text-anchor="end">blah</text>
Arguments
| :: (Foldable t, Show a1, Show a, RealFrac a, RealFrac a1) | |
| => a1 | Stroke width |
| -> LineStroke_ a | Stroke type |
| -> StrokeLineJoin_ | Stroke join type |
| -> Colour Double | Stroke colour |
| -> t (Point a) | Data |
| -> Svg |
Polyline (piecewise straight line)
> putStrLn $ renderSvg (polyline [Point 100 50, Point 120 20, Point 230 50] 4 (Dashed [3, 5]) Round C.blueviolet) <polyline points="100.0,50.0 120.0,20.0 230.0,50.0" fill="none" stroke="#8a2be2" stroke-width="4.0" stroke-linejoin="round" stroke-dasharray="3.0, 5.0" />
Arguments
| :: (Foldable t, Show a, Real o) | |
| => Colour Double | Fill colour |
| -> o | Fill opacity |
| -> t (Point a) | Contour point coordinates |
| -> Svg |
A filled polyline
> putStrLn $ renderSvg $ filledPolyline C.coral 0.3 [(Point 0 1), (Point 10 40), Point 34 50, Point 30 5] <polyline points="0,1 10,40 34,50 30,5" fill="#ff7f50" fill-opacity="0.3" />
pixel :: (Show a, RealFrac a) => [Colour Double] -> a -> a -> Scientific -> Scientific -> LabeledPoint Scientific a -> Svg Source #
pixel' :: (Show a, RealFrac a, RealFrac t) => [Colour Double] -> a -> a -> t -> t -> LabeledPoint t a -> Svg Source #
Composite plot elements
Arguments
| :: (Foldable t, Real o, Show a) | |
| => Colour Double | Fill colour |
| -> o | Fill opacity |
| -> (l -> a) | Band maximum value |
| -> (l -> a) | Band minimum value |
| -> t (LabeledPoint l a) | Centerline points |
| -> Svg |
A filled band of colour, given the coordinates of its center line
This element can be used to overlay uncertainty ranges (e.g. the first standard deviation) associated with a given data series.
Arguments
| :: (Show a, RealFrac a) | |
| => (a -> a -> Bool) | If True, fill the box with the first colour, otherwise with the second |
| -> (l -> a) | Box maximum value |
| -> (l -> a) | Box minimum value |
| -> (l -> a) | Line maximum value |
| -> (l -> a) | Line minimum value |
| -> a | Box width |
| -> a | Stroke width |
| -> Colour Double | First box colour |
| -> Colour Double | Second box colour |
| -> Colour Double | Line stroke colour |
| -> LabeledPoint l a | Data point |
| -> Svg |
A candlestick glyph for time series plots. This is a type of box glyph, commonly used in plotting financial time series.
Some financial market quantities such as currency exchange rates are aggregated over some time period (e.g. a day) and summarized by various quantities, for example opening and closing rates, as well as maximum and minimum over the period.
By convention, the candlestick colour depends on the derivative sign of one such quantity (e.g. it is green if the market closes higher than it opened, and red otherwise).
Plot utilities
axes :: (Show a, RealFrac a) => FigureData a -> Frame a -> a -> Colour Double -> Int -> Int -> Svg Source #
A pair of Cartesian axes
Arguments
| :: (Functor t, Foldable t, Show a, RealFrac a) | |
| => FigureData a | |
| -> (l -> Text) | X tick label |
| -> (l -> Text) | Y tick label |
| -> a | X label rotation angle |
| -> a | Y label rotation angle |
| -> a | Stroke width |
| -> Colour Double | Stroke colour |
| -> Maybe (t (LabeledPoint l a)) | X axis labels |
| -> Maybe (t (LabeledPoint l a)) | Y axis labels |
| -> (t (LabeledPoint l a) -> Svg) | Data rendering function |
| -> t (LabeledPoint l a) | Data |
| -> Svg |
toPlot performs a number of related operations:
- Maps the dataset to the figure frame
- Renders the X, Y axes
- Renders the transformed dataset onto the newly created plot canvas
data FigureData a Source #
Figure data
Constructors
| FigureData | |
Fields
| |
Instances
| Functor FigureData Source # | |
| Eq a => Eq (FigureData a) Source # | |
| Show a => Show (FigureData a) Source # | |
| Generic (FigureData a) Source # | |
| (Default a, Fractional a) => Default (FigureData a) Source # | |
| type Rep (FigureData a) Source # | |
Element attributes
data LineStroke_ a Source #
Specify a continuous or dashed stroke
Constructors
| Continuous | |
| Dashed [a] |
Instances
| Eq a => Eq (LineStroke_ a) Source # | |
| Show a => Show (LineStroke_ a) Source # | |
| Generic (LineStroke_ a) Source # | |
| Default (LineStroke_ a) Source # | |
| type Rep (LineStroke_ a) Source # | |
data TextAnchor_ Source #
Specify at which end should the text be anchored to its current point
Instances
Operations on frames
frameFromFigData :: Num a => FigureData a -> Frame a Source #
mkFrameOrigin :: Num a => a -> a -> Frame a Source #
Build a frame rooted at the origin (0, 0)
figFWidth :: Num a => FigureData a -> a Source #
figFHeight :: Num a => FigureData a -> a Source #
Colour utilities
blendTwo :: Colour Double -> Colour Double -> Int -> [Colour Double] Source #
`blendTwo c1 c2 n` creates a palette of n intermediate colours, interpolated linearly between c1 and c2.
palette :: [Colour Double] -> Int -> [Colour Double] Source #
`palette cs n` blends linearly a list of colours cs, by generating n intermediate colours between each consecutive pair.
SVG utilities
Create the SVG header
Arguments
| :: Fractional a | |
| => Frame a | Initial frame |
| -> Frame a | Final frame |
| -> Bool | Flip L-R in [0,1] x [0,1] |
| -> Point a | Point in the initial frame |
| -> Point a |
Move point to the SVG frame of reference (for which the origing is a the top-left corner of the screen)
toSvgFrameLP :: Fractional a => Frame a -> Frame a -> Bool -> LabeledPoint l a -> LabeledPoint l a Source #
Move LabeledPoint to the SVG frame of reference (uses toSvgFrame )
Types
A frame, i.e. a bounding box for objects
Instances
| Eq a => Eq (Frame a) Source # | |
| Show a => Show (Frame a) Source # | |
| Generic (Frame a) Source # | |
| Ord a => Semigroup (Frame a) Source # | The semigroup operation ( |
| (Ord a, Num a) => Monoid (Frame a) Source # | |
| (Default a, Num a) => Default (Frame a) Source # | |
| type Rep (Frame a) Source # | |
A Point object defines a point in the plane
data LabeledPoint l a Source #
A LabeledPoint carries a "label" (i.e. any additional information such as a text tag, or any other data structure), in addition to position information. Data points on a plot are LabeledPoints.
Constructors
| LabeledPoint | |
Fields
| |
labelPoint :: (Point a -> l) -> Point a -> LabeledPoint l a Source #
Given a labelling function and a Point p, returned a LabeledPoint containing p and the computed label
mapLabel :: (l1 -> l2) -> LabeledPoint l1 a -> LabeledPoint l2 a Source #
Apply a function to the label
Helpers
Arguments
| :: (Enum a, RealFrac a) | |
| => Frame a | |
| -> Int | Number of points along x axis |
| -> Int | " y axis |
| -> [Point a] |
A list of nx by ny points in the plane arranged on the vertices of a rectangular mesh.
NB: Only the minimum x, y coordinate point is included in the output mesh. This is intentional, since the output from this can be used as an input to functions that use a corner rather than the center point as refernce (e.g. rect)
Misc.
toFloat :: Scientific -> Float Source #
Convert a floating point value in Scientific form to Float
wholeDecimal :: (Integral a, RealFrac b) => b -> (a, b) Source #
Separate whole and decimal part of a fractional number e.g.
> wholeDecimal pi (3,0.14159265358979312)