pure-noise: High-performance composable noise generation (Perlin, Simplex, Cellular)
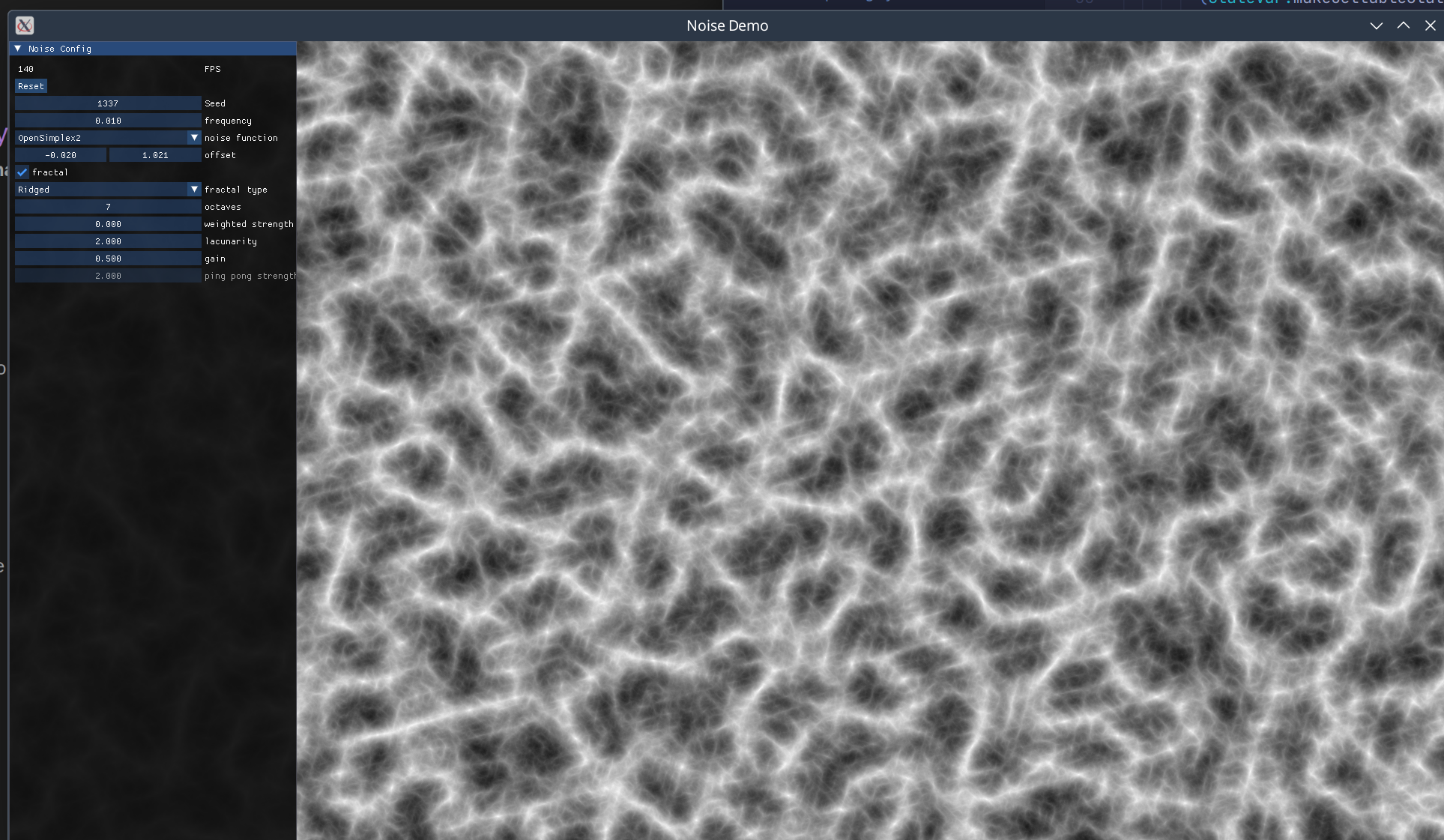
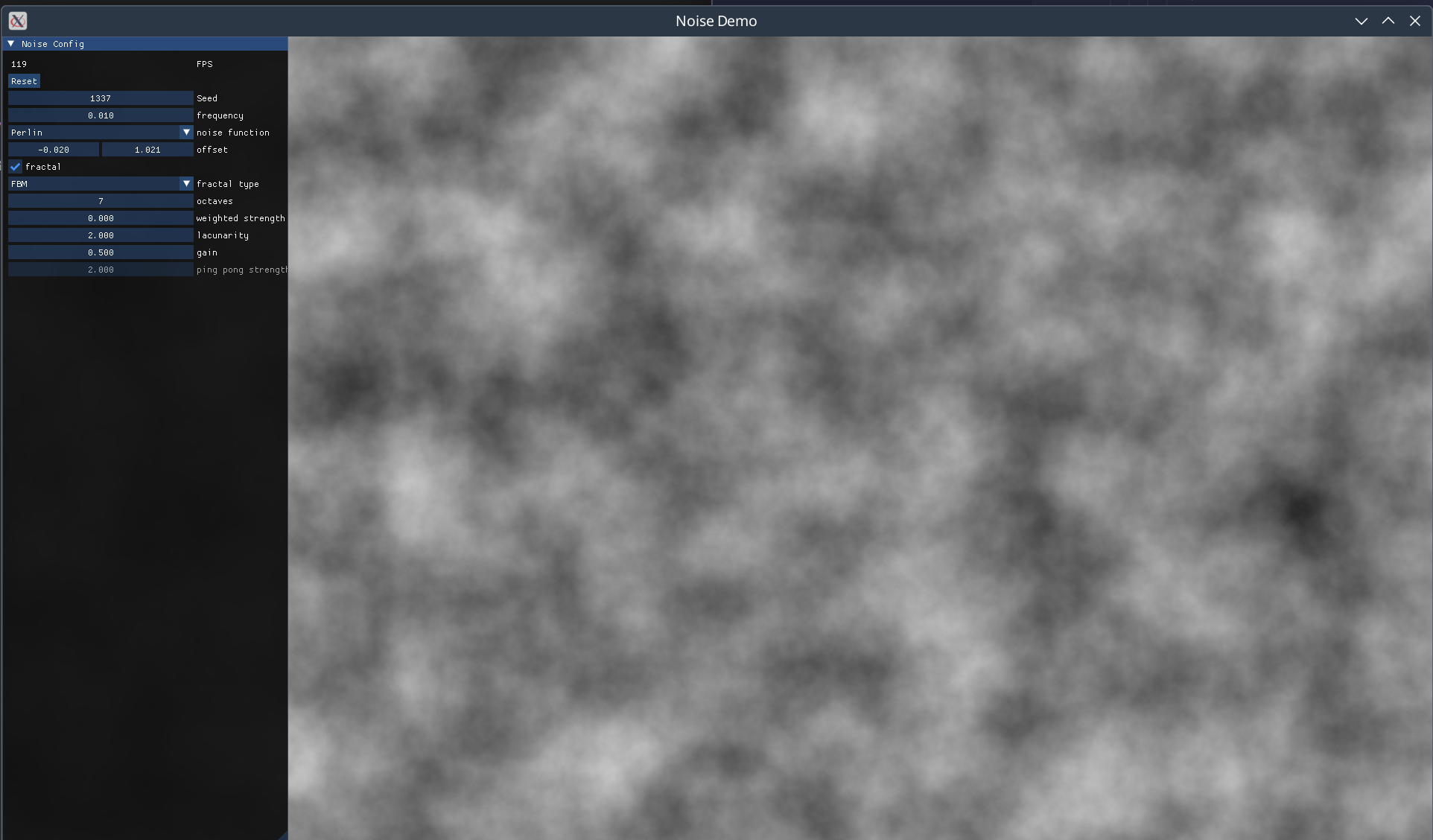
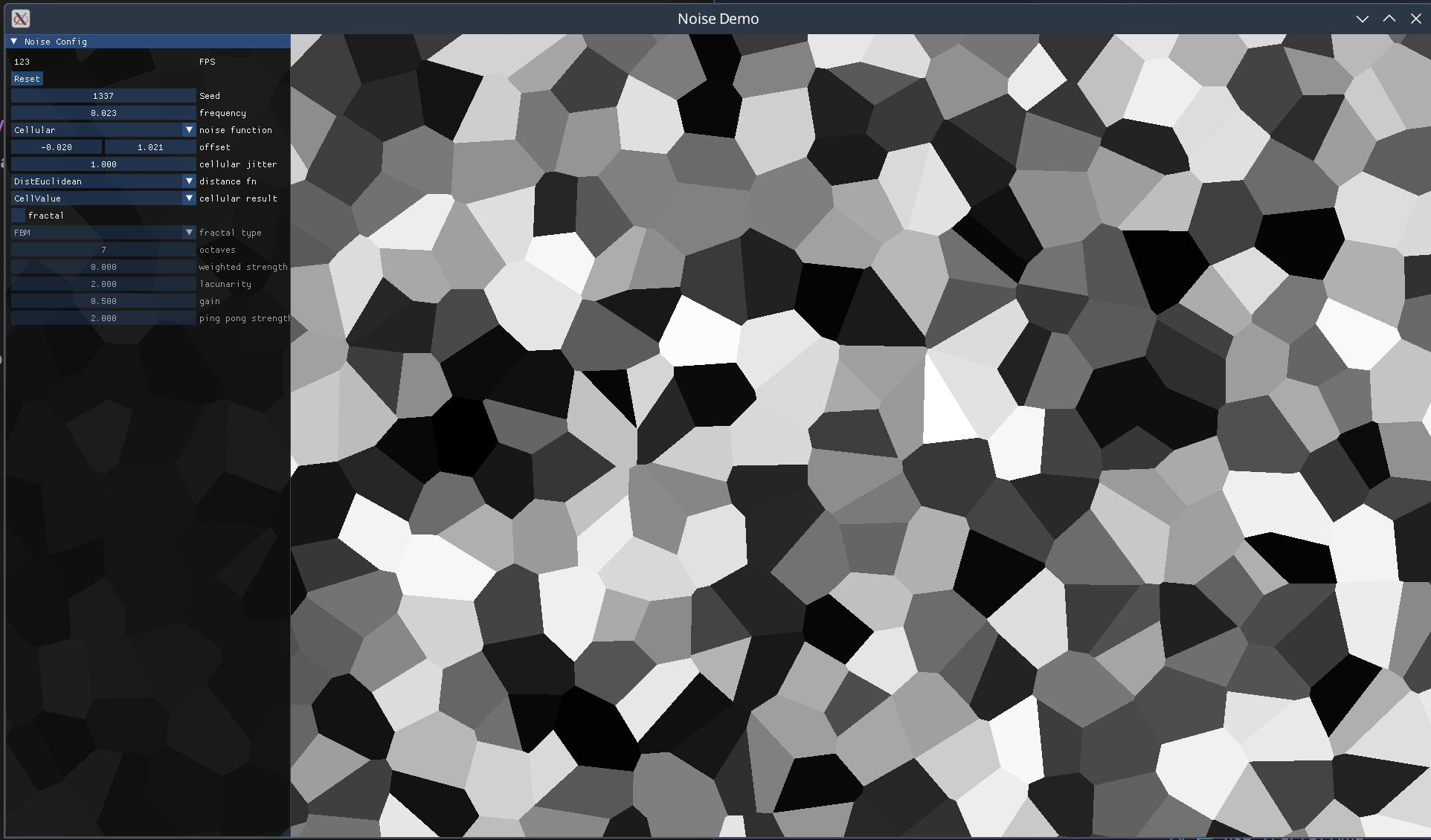
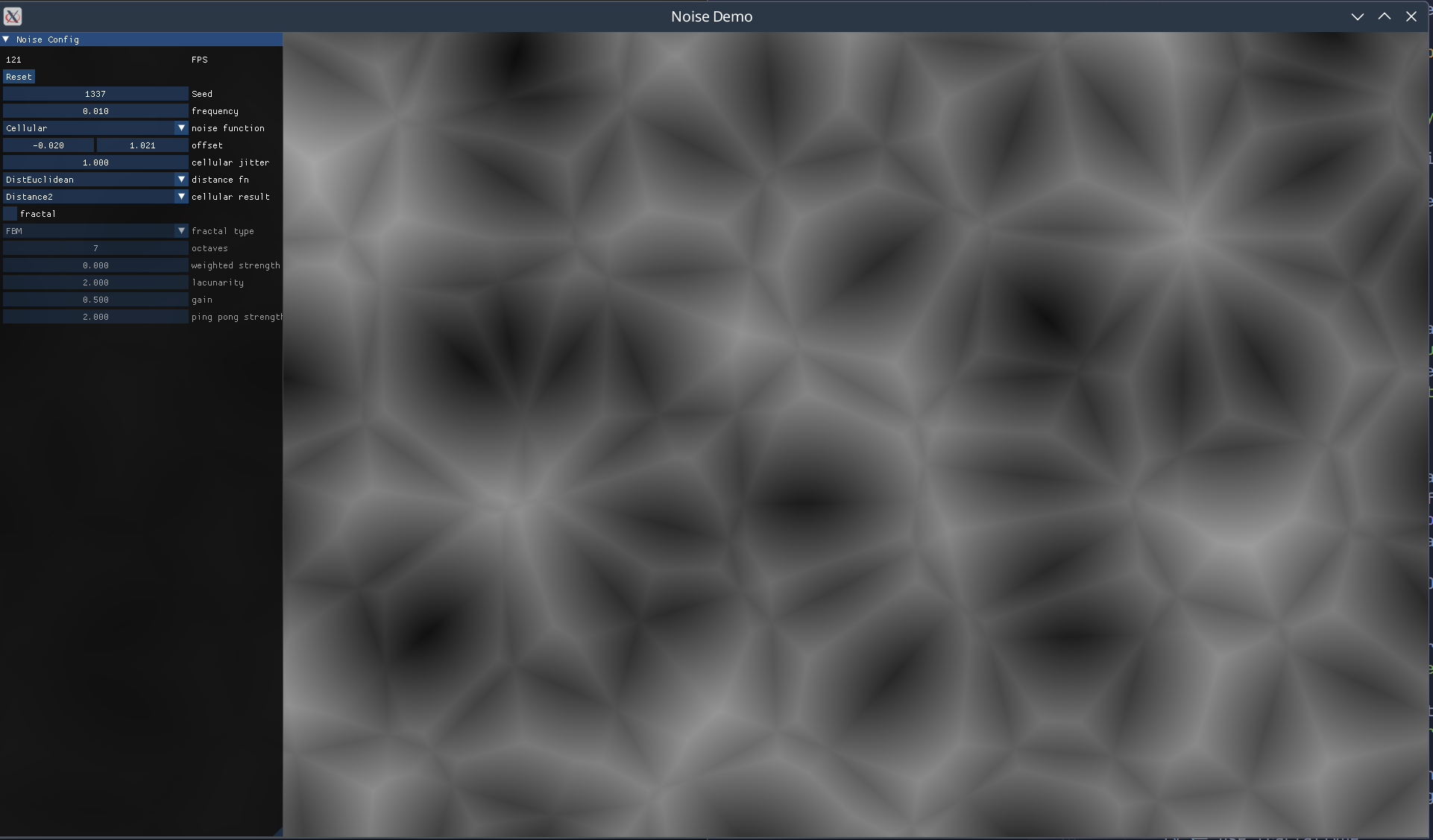
A high-performance noise generation library ported from FastNoiseLite. Provides N-dimensional noise functions (Perlin, OpenSimplex, SuperSimplex, Value, Cellular) that can be composed using Num or Fractional methods with minimal performance overhead. Noise values are generally clamped to [-1, 1]. Benefits significantly from LLVM backend compilation (~50-80% performance improvement).
[Skip to Readme]

Modules
[Index] [Quick Jump]
Downloads
- pure-noise-0.2.0.0.tar.gz [browse] (Cabal source package)
- Package description (as included in the package)
Maintainer's Corner
For package maintainers and hackage trustees
Candidates
- No Candidates
| Versions [RSS] | 0.1.0.0, 0.1.0.1, 0.2.0.0 |
|---|---|
| Change log | CHANGELOG.md |
| Dependencies | base (>=4.16 && <5), primitive (>=0.8 && <0.10) [details] |
| License | BSD-3-Clause |
| Copyright | 2024 Jeremy Nuttall |
| Author | Jeremy Nuttall |
| Maintainer | jeremy@jeremy-nuttall.com |
| Category | Math, Numeric, Noise |
| Home page | https://github.com/jtnuttall/pure-noise#readme |
| Bug tracker | https://github.com/jtnuttall/pure-noise/issues |
| Source repo | head: git clone https://github.com/jtnuttall/pure-noise |
| Uploaded | by jtnuttall at 2025-10-22T04:33:50Z |
| Distributions | NixOS:0.1.0.1 |
| Downloads | 76 total (10 in the last 30 days) |
| Rating | (no votes yet) [estimated by Bayesian average] |
| Your Rating | |
| Status | Docs uploaded by user Build status unknown [no reports yet] |