| Safe Haskell | None |
|---|---|
| Language | Haskell2010 |
TypedSession.Driver
Description
Schematic diagram of the communication structure of three roles through typed-session:
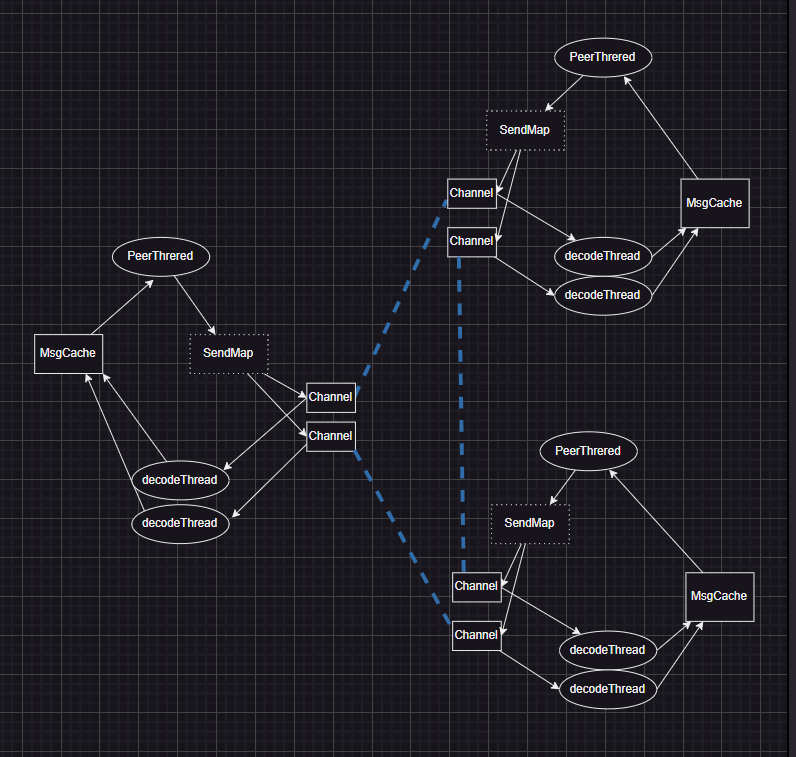
Some explanations for this diagram:
- Roles are connected through channels, and there are many types of channels, such as channels established through TCP or channels established through TMVar.
- Each role has a Peer thread, in which the Peer runs.
- Each role has one or more decode threads, and the decoded Msgs are placed in the MsgCache.
Synopsis
- data Driver role' ps (m :: Type -> Type) = Driver {
- sendMsg :: forall (send :: role') (recv :: role') (st :: ps) (st' :: ps) (st'' :: ps). (SingI recv, SingI st, SingToInt ps, SingToInt role') => Sing recv -> Msg role' ps st send st' recv st'' -> m ()
- recvMsg :: forall (st' :: ps). SingToInt ps => Sing st' -> m (AnyMsg role' ps)
- terminalDecodeThreads :: [m ()]
- runPeerWithDriver :: forall role' ps (r :: role') (st :: ps) m a. (Monad m, SingToInt role') => Driver role' ps m -> Peer role' ps r m (At a (Done r :: ps)) st -> m a
- data TraceSendRecv role' ps where
- TraceSendMsg :: forall role' ps. AnyMsg role' ps -> TraceSendRecv role' ps
- TraceRecvMsg :: forall role' ps. AnyMsg role' ps -> TraceSendRecv role' ps
- type Tracer role' ps (m :: Type -> Type) = TraceSendRecv role' ps -> m ()
- nullTracer :: Monad m => a -> m ()
- type ConnChannels role' (m :: Type -> Type) bytes = [(SomeRole role', Channel m bytes)]
- data NotConnect role' = NotConnect role'
- data SomeRole role' = SingToInt role' => SomeRole (Sing r)
- driverSimple :: forall role' ps failure bytes m n. (Monad m, Monad n, MonadSTM n, MonadFork n, MonadDelay n, MonadThrow n, SingToInt role', Enum role', Show role', Typeable role', Exception failure) => Tracer role' ps n -> Encode role' ps bytes -> Decode role' ps failure bytes -> ConnChannels role' n bytes -> (forall a. n a -> m a) -> n (Driver role' ps m)
- decodeLoop :: (Exception failure, MonadDelay n, MonadSTM n, MonadThrow n) => Maybe bytes -> Decode role' ps failure bytes -> Channel n bytes -> MsgCache role' ps n -> n ()
- localDriverSimple :: forall role' ps m n. (Monad m, Monad n, MonadSTM n, Enum role', MonadThrow n, Show role', Typeable role') => Tracer role' ps n -> IntMap (MsgCache role' ps n) -> SomeRole role' -> (forall a. n a -> m a) -> Driver role' ps m
Documentation
data Driver role' ps (m :: Type -> Type) Source #
Contains two functions sendMsg, recvMsg. runPeerWithDriver uses them to send and receive Msg.
Constructors
| Driver | |
Fields
| |
runPeerWithDriver :: forall role' ps (r :: role') (st :: ps) m a. (Monad m, SingToInt role') => Driver role' ps m -> Peer role' ps r m (At a (Done r :: ps)) st -> m a Source #
Interpret Peer.
data TraceSendRecv role' ps where Source #
A wrapper around AnyMsg that represents sending and receiving Msg.
Constructors
| TraceSendMsg :: forall role' ps. AnyMsg role' ps -> TraceSendRecv role' ps | |
| TraceRecvMsg :: forall role' ps. AnyMsg role' ps -> TraceSendRecv role' ps |
Instances
| Show (AnyMsg role' ps) => Show (TraceSendRecv role' ps) Source # | |
Defined in TypedSession.Driver Methods showsPrec :: Int -> TraceSendRecv role' ps -> ShowS # show :: TraceSendRecv role' ps -> String # showList :: [TraceSendRecv role' ps] -> ShowS # | |
type Tracer role' ps (m :: Type -> Type) = TraceSendRecv role' ps -> m () Source #
Similar to the log function, used to print received or sent messages.
nullTracer :: Monad m => a -> m () Source #
The default trace function. It simply ignores everything.
type ConnChannels role' (m :: Type -> Type) bytes = [(SomeRole role', Channel m bytes)] Source #
ConnChannels aggregates the multiple connect channels together.
data NotConnect role' Source #
Constructors
| NotConnect role' |
Instances
| (Show role', Typeable role') => Exception (NotConnect role') Source # | |
Defined in TypedSession.Driver Methods toException :: NotConnect role' -> SomeException # fromException :: SomeException -> Maybe (NotConnect role') # displayException :: NotConnect role' -> String # backtraceDesired :: NotConnect role' -> Bool # | |
| Show role' => Show (NotConnect role') Source # | |
Defined in TypedSession.Driver Methods showsPrec :: Int -> NotConnect role' -> ShowS # show :: NotConnect role' -> String # showList :: [NotConnect role'] -> ShowS # | |
driverSimple :: forall role' ps failure bytes m n. (Monad m, Monad n, MonadSTM n, MonadFork n, MonadDelay n, MonadThrow n, SingToInt role', Enum role', Show role', Typeable role', Exception failure) => Tracer role' ps n -> Encode role' ps bytes -> Decode role' ps failure bytes -> ConnChannels role' n bytes -> (forall a. n a -> m a) -> n (Driver role' ps m) Source #
Build Driver through ConnChannels. Here we need some help from other functions:
- `Tracer role' ps n` is similar to the log function, used to print received or sent messages.
- `Encode role' ps` bytes encoding function, converts Msg into bytes.
- `Decode role' ps failure bytes` bytes decode function, converts bytes into Msg.
- `forall a. n a -> m a` This is a bit complicated, I will explain it in detail below.
I see Peer as three layers:
Peerupper layer, meets the requirements of McBride Indexed Monad, uses do syntax construction, has semantic checks, and is interpreted to the second layer m through runPeerWithDriver.mmiddle layer, describes the business requirements in this layer, and converts the received Msg into specific business actions.nbottom layer, responsible for receiving and sending bytes. It can have multiple options such as IO or IOSim. Using IOSim can easily test the code.
decodeLoop :: (Exception failure, MonadDelay n, MonadSTM n, MonadThrow n) => Maybe bytes -> Decode role' ps failure bytes -> Channel n bytes -> MsgCache role' ps n -> n () Source #
decode loop, usually in a separate thread.
The decoded Msg is placed in MsgCache.
data Msg role' ps (from :: ps) (sendAndSt :: (role', ps)) (recvAndSt :: (role', ps))
Note that when placing a new Msg in MsgCache, if a Msg with the same from already exists in MsgCache, the decoding process will be blocked,
until that Msg is consumed before placing the new Msg in MsgCache.
This usually happens when the efficiency of Msg generation is greater than the efficiency of consumption.