cleff - fast and concise extensible effects


cleff is an extensible effects library for Haskell, with a focus on the balance of performance, expressiveness and ease of use. It provides a set of predefined effects that you can conveniently reuse in your program, as well as low-boilerplate mechanisms for defining and interpreting new domain-specific effects on your own.
In essence, cleff offers:
-
Performance:
cleff does not use techniques like Freer monads or monad transformers. Instead, cleff's Eff monad is essentially implemented as a ReaderT IO. This concrete formulation allows more GHC optimizations to fire, and has lower performance overhead. In microbenchmarks, cleff outperforms polysemy and even mtl.
The only caveat is that cleff does not support nondeterminism and continuations in the Eff monad - but after all, most effects libraries has broken nondeterminism support, and we encourage users to wrap another monad transformer with support of nondeterminism (e.g. ListT) over the main Eff monad in such cases.
-
Low boilerplate:
cleff supports user-defined effects and provides simple yet flexible API for implementing them. Implementations of effects are simply case-splitting functions, and users familiar with polysemy or freer-simple will find it very easy to get along with cleff. Take a look at the examples.
-
Interoperability:
cleff's simple underlying structure allows us to implement near-seamless interop with the current ecosystem, mainly classes like MonadUnliftIO, MonadCatch and MonadBaseControl. In other words, you can directly use libraries like unliftio, exceptions and lifted-async in cleff without writing any "adapter" code.
-
Predictable semantics:
Traditional effect libraries have many surprising behaviors. For example, mtl reverts the state when an error is thrown, and has a lot more subtleties when interacting with IO. cleff implements State and Writer as IORef operations, and Error as Exceptions, so it is able to interact well with IO and provide semantics that are predictable in the presence of concurrency and exceptions. Moreover, any potentially surprising behavior is carefully documented for each effect.
-
Higher-order effects:
Higher-order effects are effects that "wraps" monadic computations, like local, catchError and mask. Implementing higher-order effects is often tedious, or outright not supported in most effect libraries. polysemy is the first library that aims to provide easy higher-order effects mechanism with its Tactics API. Following its path, cleff provides a set of combinators that can be used to implement higher-order effects. These combinators are as expressive as polysemy's, and are also easier to use correctly.
-
Ergonomics without sacrificing flexibility:
Unlike mtl, cleff doesn't have functional dependencies on effects, so you can have e.g. multiple State effects. As a side effect, GHC will sometimes ask you to provide which effect you're operating on via TypeApplications, or otherwise the effect usage will be ambiguous. This can be verbose at times, and we have a solution for that: cleff-plugin is a GHC plugin that works like mtl's functional dependencies, and can resolve most type ambiguities involving effects for you.
Example
This is the code that defines the classic Teletype effect. It only takes 20 lines to define the effect and two interpretations, one using stdio and another reading from and writing to a list:
import Cleff
import Cleff.Input
import Cleff.Output
import Cleff.State
import Data.Maybe (fromMaybe)
-- Effect definition
data Teletype :: Effect where
ReadTTY :: Teletype m String
WriteTTY :: String -> Teletype m ()
makeEffect ''Teletype
-- Effect Interpretation via IO
runTeletypeIO :: IOE :> es => Eff (Teletype : es) a -> Eff es a
runTeletypeIO = interpretIO \case
ReadTTY -> getLine
WriteTTY s -> putStrLn s
-- Effect interpretation via other pure effects
runTeletypePure :: [String] -> Eff (Teletype : es) w -> Eff es [String]
runTeletypePure tty = fmap (reverse . snd)
. runState [] . outputToListState
. runState tty . inputToListState
. reinterpret2 \case
ReadTTY -> fromMaybe "" <$> input
WriteTTY msg -> output msg
-- Using the effect
echo :: Teletype :> es => Eff es ()
echo = do
x <- readTTY
if null x then pure ()
else writeTTY x >> echo
echoPure :: [String] -> [String]
echoPure input = runPure $ runTeletypePure input echo
main :: IO ()
main = runIOE $ runTeletypeIO echo
See example/ for more examples.
Benchmarks
These are the results of effectful's microbenchmarks, compiled by GHC 8.10.7. Each diagram shows the average run time of each effect library's implementation of an identical program; lower is better. Each benchmark suite has two flavors - shallow and deep - where the shallow variant only uses necessary effects, and the deep variant adds 10 redundant Reader effects, to simulate more realistic scenarios. Keep in mind that these are very short and synthetic programs, and may or may not tell the accurate performance characteristics of different effect libraries in real use.
countdown: 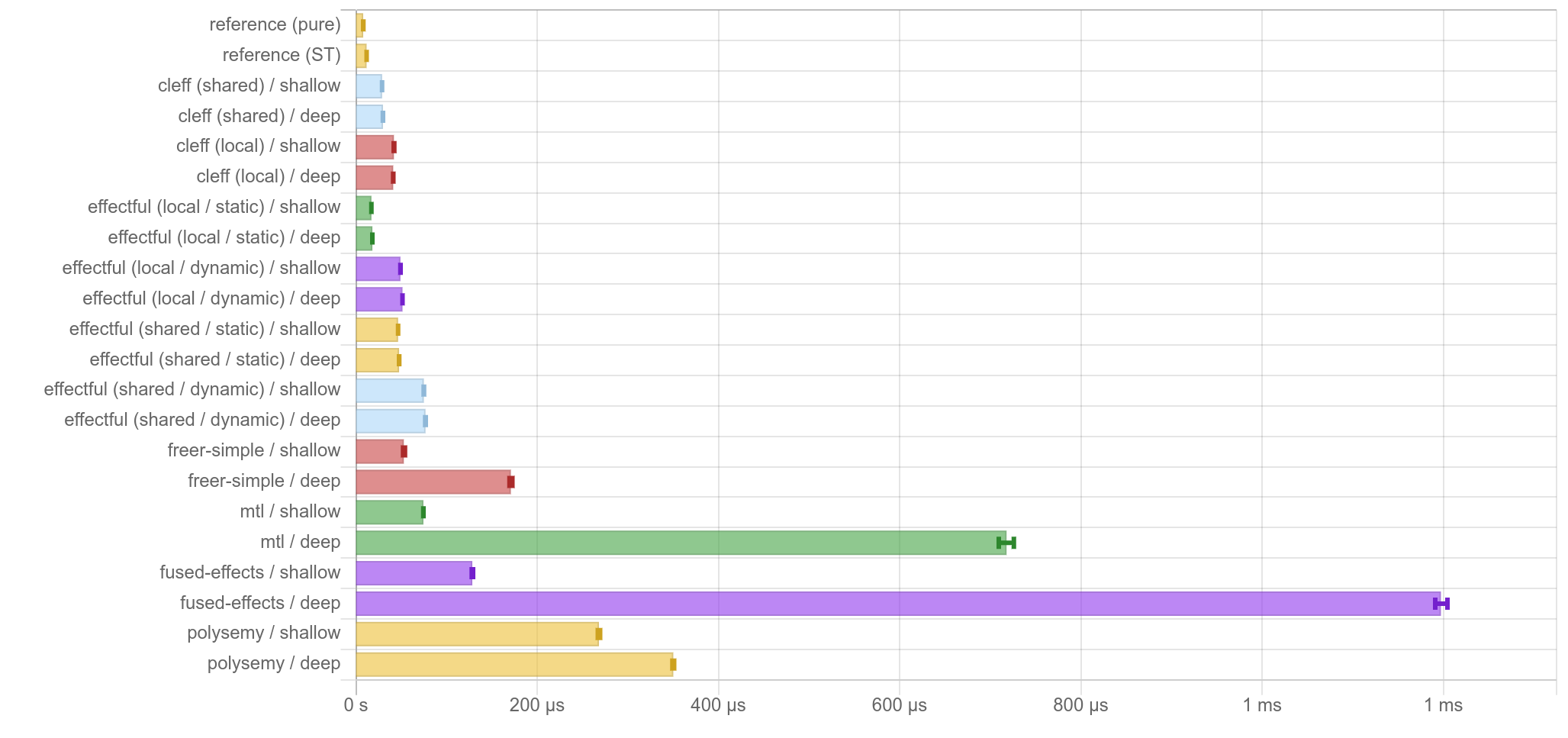
filesize: 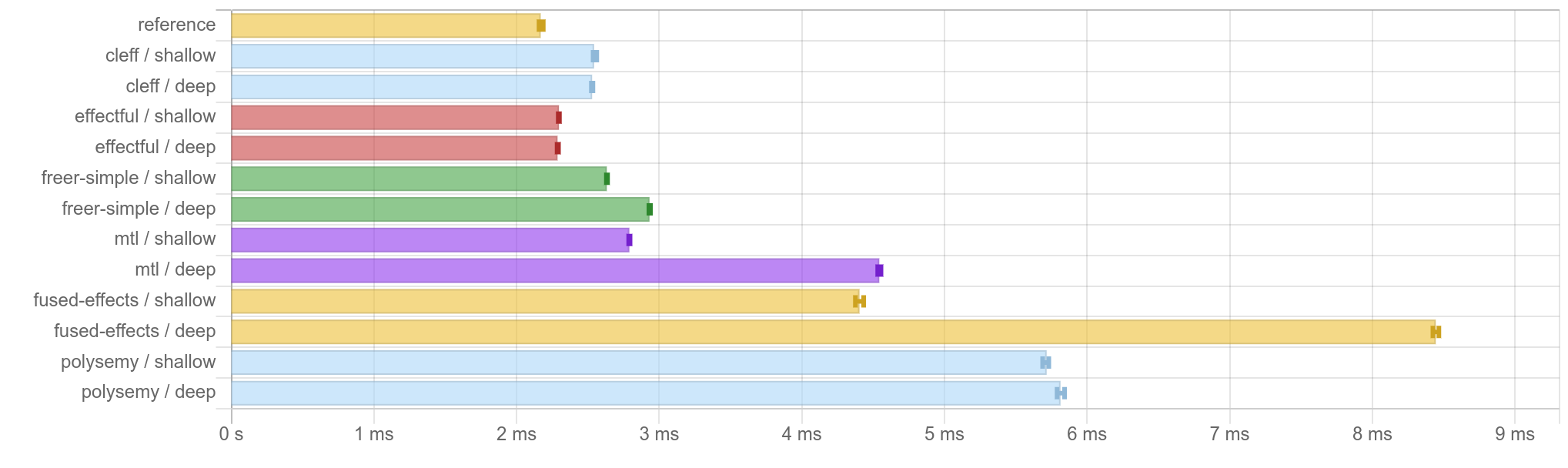
Differences from effectful
If you know about effectful, you may notice that cleff and effectful seem to make many similar claims and have a similar underlying implementation. In microbenchmarks, cleff is slightly behind effectful. This may make you confused about the differences between the two libraries. To put it simply, cleff has a more versatile and expressive effect interpretation mechanism, and a lighter weight API. In contrast, effectful gains its performance advantage by providing static dispatch for some internal effects, which means they cannot have multiple interpretations.
References
These are the useful resources that inspired this library's design and implementation.
Papers:
Libraries:
eff by Alexis King and contributors.
effectful by Andrzej Rybczak and contributors.
freer-simple by Alexis King and contributors.
polysemy by Sandy Maguire and contributors.
Talks:
Blog posts:




