lima
Sync your README with your Haskell codebase.
Convert files between:
Haskell (.hs)
Literate Haskell (.lhs)
GitHub Flavored Markdown (.md)
TeX (.tex)
-
LiterateMarkdown - lima is a fork of this abandoned project.
-
pandoc - supports Literate Haskell and a ton of other formats.
-
IHaskell - create Jupyter notebooks with Haskell code cells and GitHub Flavored Markdown text cells.
-
lhs2tex - convert Literate Haskell to TeX.
-
agda2lagda - Generate a literate Agda/Haskell script from an Agda/Haskell script. Produces LaTeX or Markdown literate scripts.
-
markdown-unlit - markdown-unlit is a custom unlit program. It can be used to extract Haskell code from Markdown files.
-
unlit - Tool to convert literate code between styles or to code.
-
design-tools - a Pandoc filter for building a book from Markdown.
Scope
lima focuses on converting documents between formats and allows to concatenate documents.
Other scenarios, e.g., inlining a document into a document, may require specialized tools.
Demo
Markdown
.hs and .md
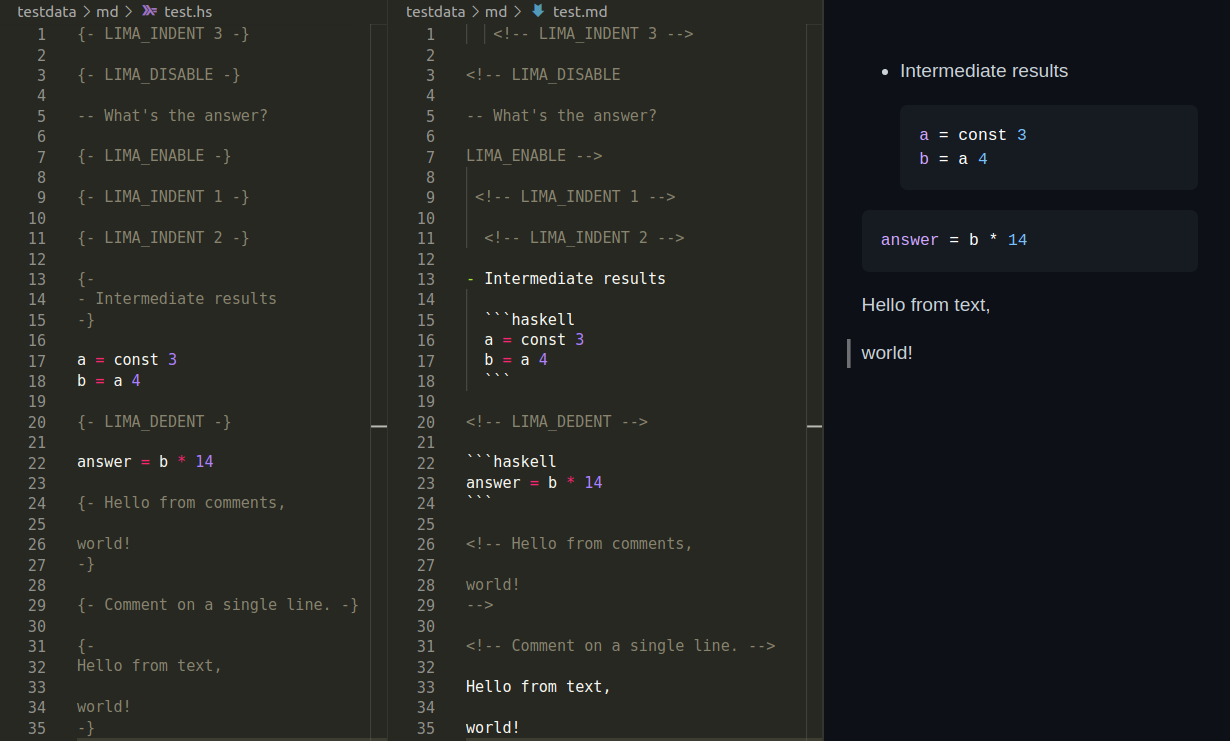
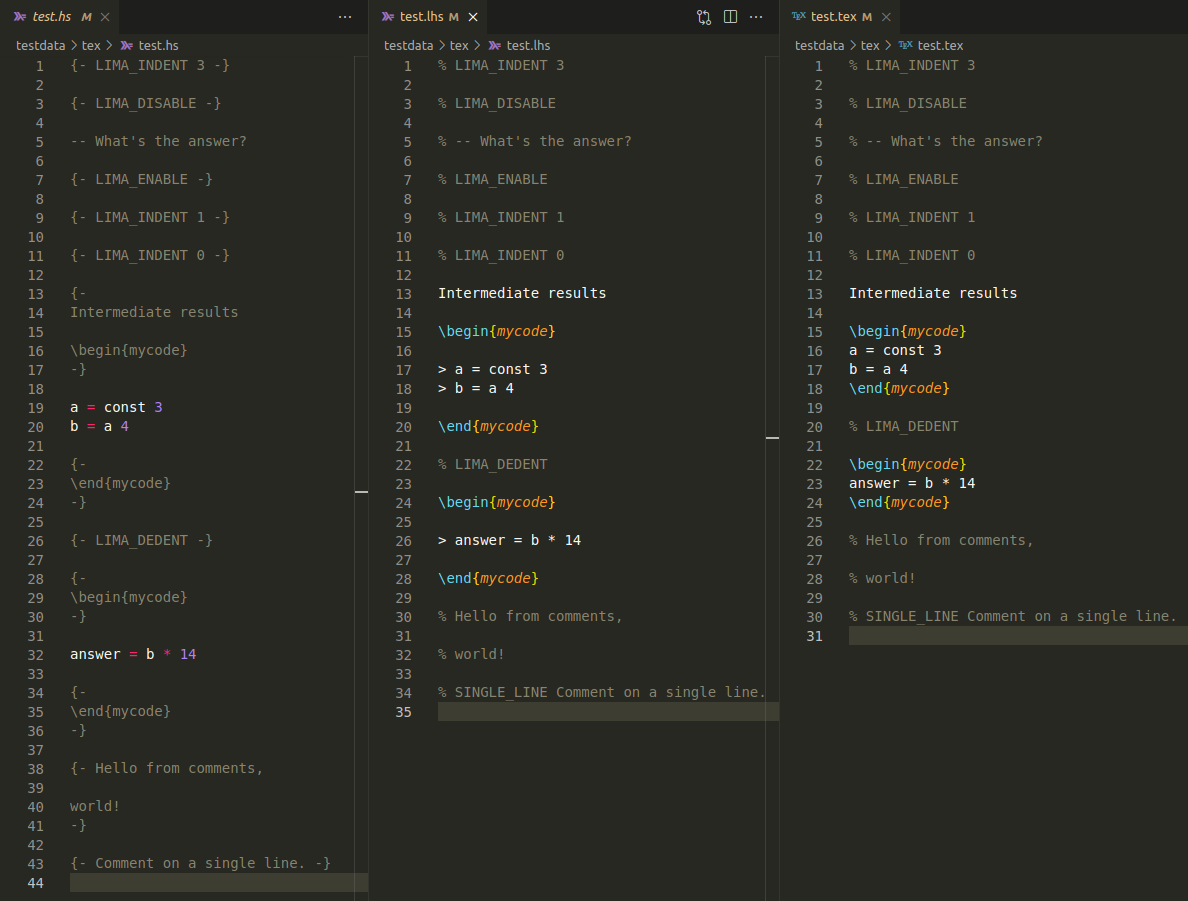
TeX
.hs and .lhs and .tex
Ideas
- A document is a text in a supported format.
- I introduced tags into supported formats.
- E.g., in
.hs documents, tags are multiline comments written on a single line like '{- LIMA_ENABLE -}'.
- Tag names are configurable.
- A user may set '
on' instead of 'LIMA_ENABLE'.
- A document can be parsed into a list of tokens.
- Tags affect document parsing.
- The tokens can be printed back to that document.
- Formatting a document is printing a parsed document back to itself.
- Formatting is idempotent. In other words, formatting the document again won't change its content.
- The
lima library provides a parser and a printer for each supported format.
- A composition of a printer after a parser produces a converter.
- Such a converter is usually invertible for a formatted document.
- Converting a document
A to a document B, then converting B to A doesn't change the content of A.
Suggested setup
-
Create a test suite. README.hs may be its main file.
-
Add lima and text to its dependencies.
-
Create a test module. It may have the following content.
import Lima.Converter (Format (..), convertTo, def)
import Data.Text.IO qualified as T
main :: IO ()
main = T.readFile "README.hs" >>= T.writeFile "README.md" . (Hs `convertTo` Md) def
This package has three such test suites:
Suggested workflow
Here's a suggested workflow for Haskell and Markdown:
- Edit the code in a
README.hs using Haskell Language Server.
- Convert
README.hs to a README.md. Comments from README.hs become text in README.md.
- Edit the text in
README.md using markdownlint.
- Convert
README.md back to the README.hs to keep files in sync. Text from README.md becomes comments in README.hs.
- Repeat.
Contribute
Clone this repo and enter lima.
git clone https://github.com/deemp/lima
cd lima
cabal
Build
cabal update
cabal build
nix
-
Install Nix.
-
Run a devshell and build lima using the project's cabal:
nix develop nix-dev/
cabal build
-
Optionally, start VSCodium:
nix run nix-dev/#writeSettings
nix run nix-dev/#codium .
-
Open a Haskell file there, hover over a term and wait until HLS shows hints.
-
Troubleshoot if necessary.



